Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act: What Virginia Businesses Must Know
by Zain Noor, Last updated: November 25, 2025, ref:

Data privacy laws are getting stricter every year. Customers expect companies to protect their personal information, and businesses in Virginia must now comply with the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA). This law gives residents more control over their data and requires organizations to manage that data responsibly.
A recent Cisco Privacy Study found that most consumers choose companies that protect their data. This means VCDPA compliance is not only a legal requirement it also builds trust, protects your reputation, and reduces risk.
This guide explains the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act in simple terms and shows how your business can meet its requirements without confusion.
What Is the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA)?
The Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act is a state privacy law that took effect on January 1, 2023. It gives Virginia residents several rights over their personal information and sets rules for how companies must collect, store, use, and share that information.
Although the VCDPA is similar to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), it has its own unique requirements that businesses must understand clearly.
Does the VCDPA Apply to Your Business?
Your business must comply with the VCDPA if it meets one of these conditions:
Condition 1
You process personal data of 100,000 or more Virginia residents in a year.
Condition 2
You process personal data of 25,000 or more residents, and more than half of your revenue comes from selling personal data.
If your business operates online, handles customer accounts, collects form data, or manages digital content from Virginia residents, you should check whether you fall into one of these categories.
Step 1: Audit Your Data
To comply with the VCDPA, start by understanding what data you have and how you use it.
What to review:
• What personal data do you collect
• Why do you collect it
• Where it is stored
• Who has access to it
• How long do you keep it
• Which third parties process or store it
This step helps you follow the law’s data minimization rule: only collect data that you truly need.
Step 2: Support Consumer Data Rights
The VCDPA gives residents several rights. Your business must be able to respond to these requests within 45 days.
Rights under the VCDPA:
- Right to access their personal data
- Right to correct inaccurate data
- Right to delete their data
- Right to receive a copy of their data
- Right to opt out of:
- Targeted advertising
- Sale of personal data
- Profiling that affects them significantly
What your business must do:
• Provide a simple way for users to submit requests
• Verify their identity for security
• Respond quickly and consistently
• Have internal workflows to process each request
Businesses that manage videos, audio recordings, call recordings, or scanned documents often find this challenging because personal data is spread across many files.
Step 3: Update Your Privacy Policy
Your privacy policy must clearly explain:
• What data do you collect
• Why do you collect it
• Whether you share or sell it
• Whether you use it for targeted advertising
• How customers can exercise their rights
Use clear language. Keep the policy easy to locate on your website or application.
Step 4: Conduct Data Protection Assessments (DPAs)
A Data Protection Assessment (DPA) is required when your business performs high-risk data activities.
High-risk examples:
• Targeted advertising
• Selling personal information
• Profiling that impacts a person’s access to services
• Processing sensitive personal data
• Handling large volumes of unstructured content (videos, documents, emails)
Your DPA should include:
• Why are you processing the data
• Risks involved
• How do you reduce those risks
• Whether safer alternatives exist
• Documentation for audits
DPAs are often overlooked, but are a key requirement under the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act.
Step 5: Train Your Team
Every department that handles personal data must understand:
• The basics of the VCDPA
• How to avoid data misuse
• How to process customer requests
• How to report a suspected issue
• How to identify high-risk data workflows
Regular training reduces mistakes and improves compliance.
Step 6: Maintain Ongoing Compliance
Compliance is not a one-time task. Your business must regularly:
• Review privacy practices
• Update third-party contracts
• Refresh internal policies
• Track changes in privacy laws
• Test data security controls
• Document everything
Strong documentation is important for proving compliance during an investigation.
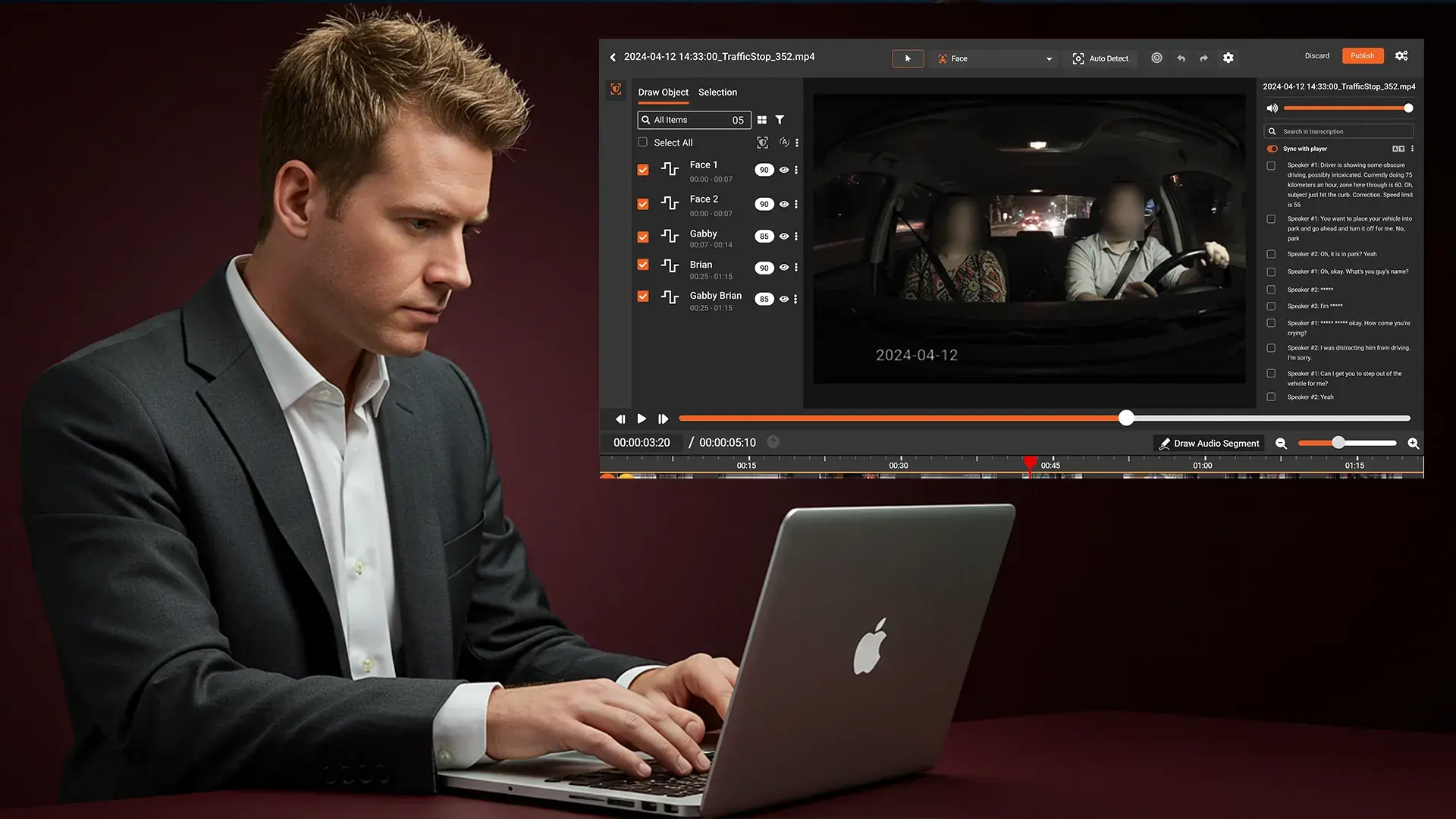
How VIDIZMO Redactor Helps with VCDPA Compliance
Most organizations today work heavily with video files, audio recordings, documents, scanned forms, and images containing personal data. Manually reviewing or editing this content is slow, costly, and prone to errors.
VIDIZMO Redactor automates this process using Artificial Intelligence (AI).
What VIDIZMO Redactor can do:
• Automatically detect and redact faces, names, license plates, and other Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and Personal Health Information (PHI)
• Redact sensitive data in videos, audio files, images, and documents
• Speed up responses to access, deletion, and correction requests
• Generate audit logs for compliance reports
• Securely store redacted and original files
• Integrate easily into existing workflows and storage systems
VIDIZMO Redactor helps businesses comply with the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act by making sensitive information safe before sharing, storing, or releasing it.
Staying Compliant with the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act
Compliance with the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act is essential for protecting customer trust and reducing legal risk. By understanding your data, updating your policies, and automating your workflows, you can meet the law’s requirements effectively.
VIDIZMO Redactor provides AI-powered tools that reduce the burden of manual redaction and help businesses stay compliant while working with large volumes of sensitive digital content.
If you want to simplify VCDPA compliance, consider exploring how VIDIZMO Redactor can support your privacy and security needs.
People Also Ask
What is the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act?
The Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act is a state privacy law that gives residents control over their personal information and requires businesses to manage that data responsibly.
What rights do consumers have under the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act?
Consumers can access, correct, delete, and download their personal data, and they can opt out of targeted advertising, data sales, and profiling.
Who must comply with the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act?
Businesses that process data from 100,000 Virginia residents or process data from 25,000 residents and earn revenue from selling personal data must comply.
How does the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act affect targeted advertising?
The law requires businesses to offer an opt-out option for targeted advertising and clearly disclose how data is used for personalization.
What is a Data Protection Assessment in the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act?
A Data Protection Assessment is a required review of high-risk data practices to identify risks and document mitigation steps for compliance.
How does VIDIZMO Redactor support compliance with the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act?
VIDIZMO Redactor automates the detection and redaction of personal information in videos, audio files, images, and documents, helping businesses respond to data requests and protect sensitive content.
Jump to
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

Legal Redaction Software: Ensuring Data Privacy & Compliance
.webp)
Redaction Tool for Insurance Claim Adjusters: Protect Sensitive Data Without Slowing Down Claims

No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think