Body Worn Camera Redaction: Legal Requirements & Privacy Compliance
by Hammad Ahmed, Last updated: February 19, 2026, ref:

Key Takeaways
-
Manual redaction averages 8 hours per 10 minutes of footage vs 30 minutes with automation
-
Harvey, Illinois settled FOIA lawsuit for $3,750 after claiming lack of technology
-
Three legal frameworks govern BWC: FOIA exemptions, state privacy laws, DPPA requirements
-
47% of agencies use body cameras, 80% of large departments, creating massive redaction demand
-
Common failures: unredacted reflections, metadata exposure, inconsistent standards, incomplete audio
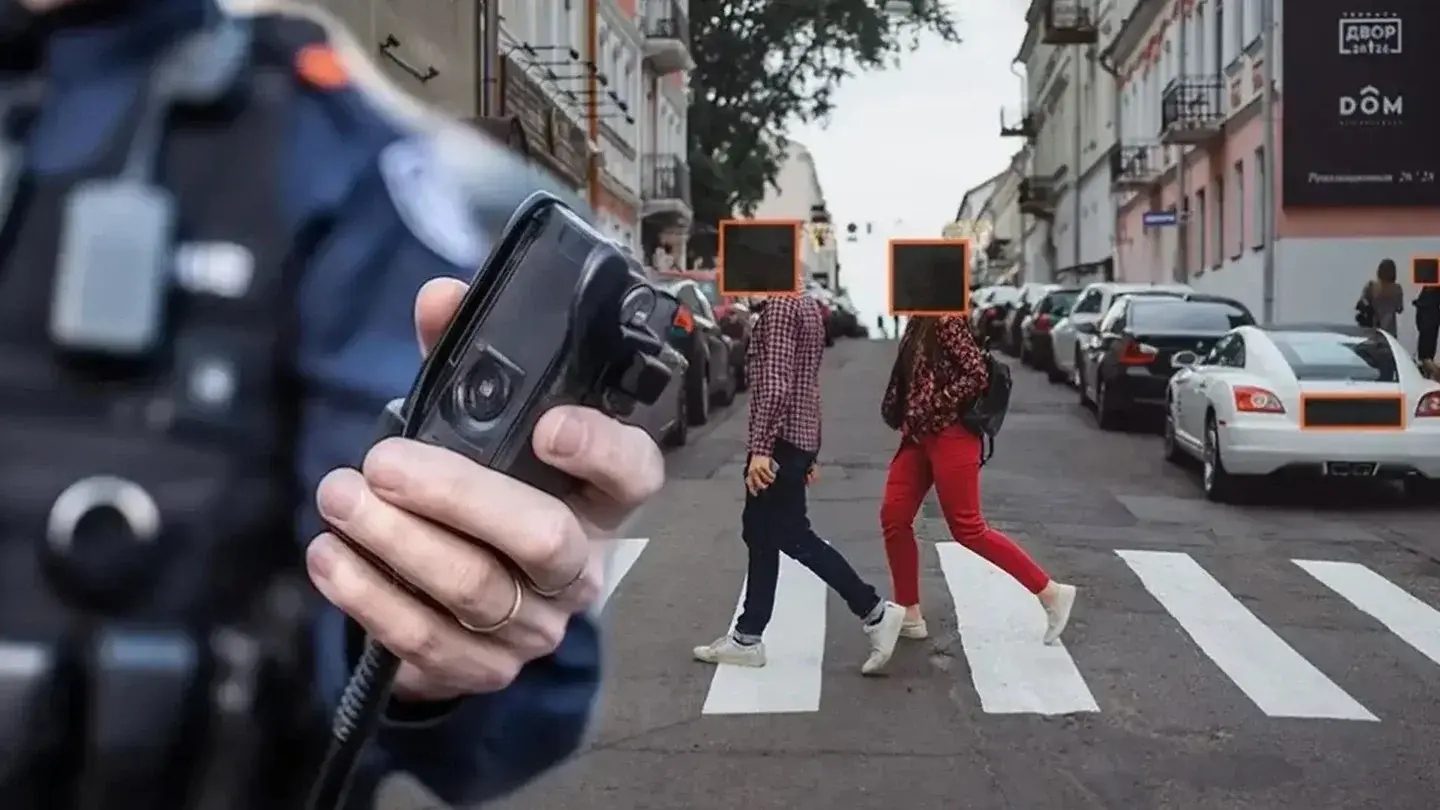
In December 2024, the City of Harvey, Illinois settled a FOIA lawsuit for $3,750 after denying a resident's request for body camera footage from his arrest. The city's defense? They "lacked the means to blur faces and protect the identities of third parties."
The lawsuit alleged "willful and intentional violations" of Illinois' Freedom of Information Act, whether from "individual subjective malfeasance or structural bad faith through underfunding and mismanagement."
This wasn't an isolated incident. Law enforcement agencies nationwide face the same challenge: body camera adoption has exploded, but redaction capabilities haven't kept pace. What appears as a simple administrative task has become a critical compliance crisis with serious legal, financial, and reputational consequences.
The Body Camera Surge Creates Redaction Bottleneck
According to the National Institute of Justice, 47% of general-purpose law enforcement agencies and 80% of large police departments have adopted body-worn cameras as of2025. This rapid deployment created an unexpected problem: agencies lack the infrastructure to handle the resulting data deluge.
Consider Seattle's 2014 experience. When the Seattle Police Department received a public records request for all dash cam videos, they discovered they had 1.6 million videos in storage. Mike Wagers, the department's chief operating officer, described the panic to NPR: "There really was, Holy cow, how are we going to fulfill this request?"
The challenge wasn't just volume. Staff would need to review those 1.6 million videos individually, examining "both the video and the audio, and then you get to a point where you need to redact some information -juvenile, sexual assault, things like that. Then you got to go frame by frame and cut that frame out."
A department with just 25 officers running body cameras 32out of every 40 hours, 46 weeks annually, generates 36,800 hours of video potentially subject to public disclosure, according to Gov1analysis. That's before considering discovery obligations owed to criminal defendants.
Why Manual Redaction Creates Systematic Failure
The fundamental problem is math. Manual body camera redaction requires a records specialist to:
- Review video frame-by-frame for faces in primary view, background, and reflections
- Manually track every individual as they move through dynamic scenes
- Identify and blur license plates on moving vehicles in varying lighting
- Locate documents, screens, or papers visible in backgrounds
- Review audio transcripts for spoken PII (names, addresses, Social Security Numbers)
- Conduct multiple quality control passes to catch oversights
Industry data confirms manual redaction typically requires an 8:1 time ratio. Secure Redact documents that redacting a 10-minute video manually takes approximately 8 hours of specialist work, while automated tools reduce this to roughly 10-30 minutes.
For a single officer's 45-minute domestic disturbance call, agencies face 36 hours of redaction work. Multiply that across hundreds of monthly incidents, and backlogs stretch from weeks into months.

The Human Factor Compounds Risk
Records specialists report cognitive fatigue after 4-6 hours of frame-by-frame review. Attention lapses during hour seven or eight lead to the oversights that generate lawsuits:
- A face visible in a mirror reflection for three seconds
- A partially obscured license plate still readable with enhancement
- An audio segment containing a witness address that wasn't muted
- Metadata embedded in the file exposing GPS coordinates
The Washington Post documented in July 2025 how Alabama's body camera law, meant to expand transparency, actually undermined police accountability due to inadequate redaction processes and accessibility barriers.
Body Camera Redaction Failure Categories
Understanding where agencies commonly fail helps build stronger prevention strategies:
-3.webp?width=1862&height=710&name=Table%20(1)-3.webp)
Legal Framework: Three Overlapping Compliance Layers
Body camera redaction isn't optional. It's legally mandated across multiple regulatory frameworks that often conflict or overlap.
Layer 1: Freedom of Information Act & State Laws
The federal Freedom of Information Act establishes the public's right to access government records. However, as the ACLU notes, there's no federal standard mandating local departments use body cameras. Current Congressional bills can only incentivize adoption through federal funding.
State laws create a complex patchwork:
California AB 748 (2018, Still Governing):
California's law requires release of critical incident footage within 45 days. The Washington Post reported agencies must redact to protect privacy while maintaining transparency. Footage must be released from incidents involving use of force, officer-involved shootings, or incidents resulting in death or great bodily harm.
Illinois Body Camera Act:
Under Illinois' Law Enforcement Officer-Worn Body Camera Act, footage is generally exempt from FOIA unless specific conditions exist: formal complaints filed, firearm discharge or force used, death or great bodily harm occurred, or officer under internal investigation.
The Better Government Association explains that flagged recordings retain for two years versus 90 days standard, creating complex retention requirements.
Washington State:
Washington presumes body camera footage is public record unless specific exemptions apply, requiring release within 45-60 days. State laws allow requesters to seek videos in bulk, creating massive processing demands.
Layer 2: Driver's Privacy Protection Act (DPPA)
The Driver's Privacy Protection Act prohibits releasing personal information obtained by state Departments of Motor Vehicles. License plates captured in body camera footage connect to DMV databases containing owner names, addresses, driver's license numbers, and medical information.
Agencies must redact license plates before public release to comply with DPPA. Redacting faces but leaving plates visible creates DPPA violations when footage is released under FOIA.
Layer 3: State Privacy Laws & Crime Victim Protections
Michigan's Law Enforcement Body-Worn Camera Privacy Act exemplifies state protections. Recordings made in private places are exempt from FOIA except under specific circumstances. Footage retained for ongoing investigations is exempt. Disclosures must comply with Crime Victim's Rights Act protections.
These state-specific protections create additional redaction requirements beyond federal law. Agencies must identify when footage captures private spaces (homes, medical facilities, vehicles) and apply heightened privacy protections.
Critical Information Requiring Redaction
Body cameras capture wide-ranging sensitive information during law enforcement interactions. Agencies must redact:
Personally Identifiable Information (PII):
- Faces and features of bystanders, witnesses, victims
- License plates and vehicle identification
- Residential addresses visible in footage
- Social Security Numbers spoken or displayed
- Identification cards (licenses, passports, documents)
Protected Health Information (PHI):
- Medical treatments, prescriptions, equipment
- Mental health crisis interventions
- Substance abuse treatment scenarios
- Healthcare provider discussions
Sensitive Case Information:
- Private conversations unrelated to incident
- Information about sexual assault, domestic violence, child abuse victims
- Confidential informant identities
- Minors in any context
- Inside views of private residences beyond necessary documentation
The University of Chicago Legal Forum notes that body camera videos "literally show' what the government is up to,'" creating strong public interest favoring disclosure. However, transparency must balance against legitimate privacy through proper redaction.
Recent Developments Affecting Redaction (2025-2026)
The regulatory landscape continues evolving rapidly.
Federal Level Updates
DHS Body Camera Expansion (February 2026):
Following two fatal shootings by federal agents in Minneapolis, Homeland Security Secretary announced federal immigration officers would start wearing body cameras "effective immediately" with nationwide expansion as funding allows.
Congressional Action:
Federal legislation would require federal officers to wear body cameras and make footage subject to FOIA. While applying only to federal officers, it signals growing standardization momentum.
State Developments
Alabama Transparency Concerns (July 2025):
Lawyers argue Alabama's body camera law, passed to expand transparency, actually undermines accountability due to access restrictions and inadequate redaction resources.
Ongoing Access Battles:
The Pulitzer Center documented obtaining footage remains difficult despite cameras' accountability purpose. Civil rights attorney Ben Crump explained: "We filed public record lawsuits constantly. But regrettably, most state supreme courts and legislatures have sided with police unions to block transparency."
The Technology Resource Dilemma
The Harvey settlement crystallizes challenges facing departments nationwide: claiming lack of technology doesn't excuse FOIA non-compliance.
First Defense Legal Aid director stated: "Every person in Illinois has aright to know what the government is doing in their name, and FOIA is the tool to hold police accountable."
Illinois Attorney General guidance explicitly states technological capability is not valid basis for denying requests. Agencies must perform redactions or obtain outside assistance.
Without redaction technology, agencies cannot comply with FOIA. But FOIA compliance is mandatory regardless of constraints. Solutions require:
- Acquiring appropriate automated tools
- Outsourcing redaction to qualified vendors
- Allocating substantial internal resources (creating other operational impacts)

Building Sustainable Redaction Programs
Agencies need comprehensive frameworks addressing policy, workflow, training, and quality control.
Essential Policy Components
Effective redaction begins with clear written policies specifying:
Presumptive Redaction:
- Faces of minors (under 18 in all contexts)
- Victims of sexual assault, domestic violence, child abuse
- Medical information and treatment scenes
- Mental health crisis subjects
- Confidential informants and protected witnesses
Case-by-Case Evaluation:
- Adult bystanders in public spaces
- Non-sensitive residential interiors
- Officer discussions not related to investigation
Generally Not Redacted:
- Public officials acting in official capacity
- Officer faces during public interactions
- Public spaces and exteriors
- Subjects actively committing observable crimes
One agency created a decision tree flowchart posted at every workstation, reducing redaction decision time by 40% and improving consistency across specialists handling similar cases.
Quality Control Requirements
Multi-layer verification ensures accuracy:
Initial Review: Specialist conducts comprehensive redaction following policy, documents exemption justifications, creates quality control checklist.
Supervisory Spot-Checks: Supervisor reviews 20% of completed redactions through random selection, approves release for high-profile cases, provides quality assurance sign-off.
Random Audits: Monthly sampling of 5% of released footage by independent quality control, findings fed back to specialists, trends analyzed for training needs.
Agencies implementing this framework reduced error rates from 3-5% to below 1% within 90 days.
Understanding Automated Redaction Technology
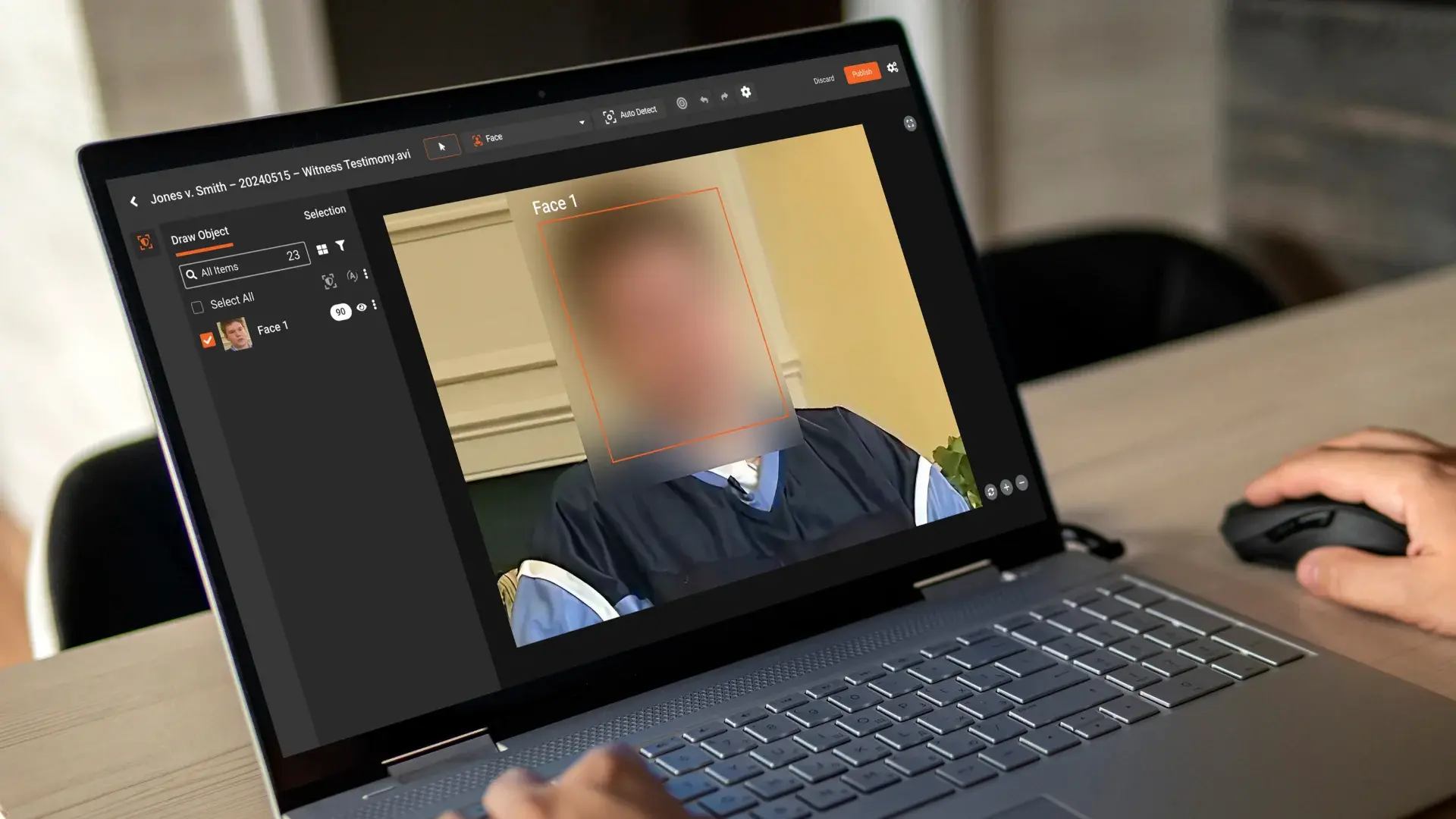
The technology gap separates agencies drowning in backlogs from those meeting compliance deadlines. Modern AI-powered platforms use:
Computer Vision Algorithms:
- Automatically detect and track faces across moving video
- Identify license plates in varying lighting and angles
- Recognize objects requiring redaction (weapons, documents, screens)
- Track individuals through complex scenes with multiple people
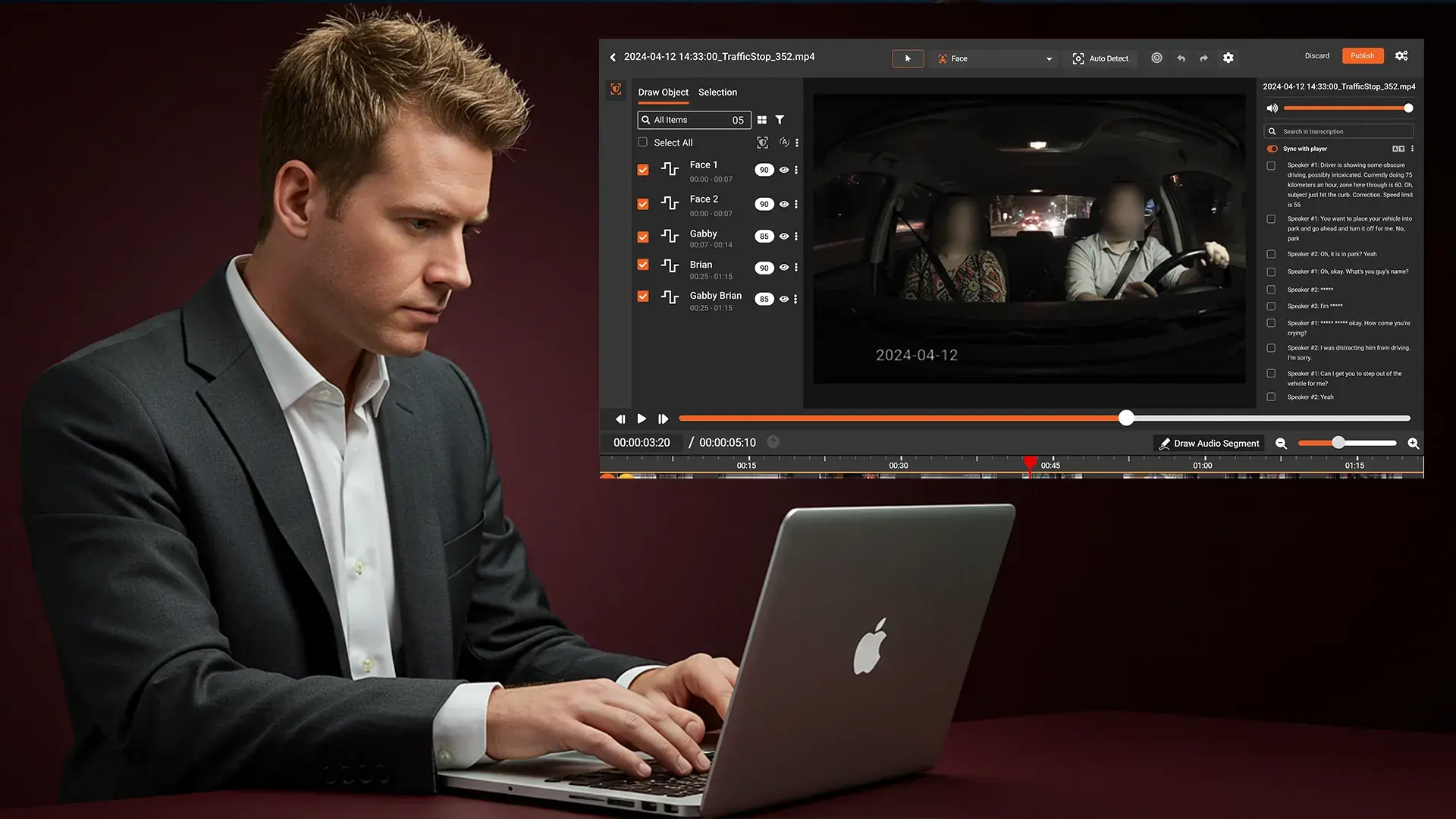
Natural Language Processing:
- Generate speech-to-text transcripts
- Identify spoken PII (names, addresses, phone numbers, SSNs)
- Flag sensitive conversation segments
- Support redaction in 40+ languages
Batch Processing Capabilities:
- Handle multiple files simultaneously
- Apply consistent standards across footage
- Scale efficiently as evidence volumes grow
- Process during off-hours without human supervision
Secure Redact documents the ability to redact a 10-minute video in approximately 10minutes using automated tools, compared to 8 hours manually. This represents an 85-90% time reduction while improving consistency.
The Hybrid Approach
Best practices combine automation with human judgment:
- Automated Initial Detection: AI identifies all faces, plates, potential PII
- Specialist Review: Human evaluates automated redactions for accuracy
- Manual Additions: Specialist catches items automation missed
- Supervisory Approval: Final review before release
This hybrid approach delivers automation speed while preserving human oversight for complex judgment calls. It reduces the 8:1manual ratio to approximately 1:1 or better.

Common Mistakes Agencies Must Avoid
Understanding typical failures helps build stronger programs.
Mistake 1: Inadequate Initial Redaction
Under-redaction occurs when sensitive information isn't properly obscured:
- Faces visible in mirrors, vehicle windows, reflective surfaces
- Partially obscured license plates still readable with enhancement
- Audio containing spoken PII not muted despite visual redaction
- Documents or screens visible in background not blurred
Prevention: Use automated detection with high sensitivity, implement multi-pass review, create reflection-specific checklists, conduct random quality audits.
Mistake 2: Metadata Exposure
Digital files contain metadata beyond visible content:
- GPS coordinates embedded in files exposing incident locations
- Timestamps revealing officer schedules and patrol patterns
- Device IDs connecting footage to specific officers
- Edit history showing original unredacted content
Prevention: Use tools that automatically strip metadata, implement file sanitization procedures, export in clean formats, verify with forensic tools before release.
Mistake 3: Inconsistent Application
Different standards for similar cases create legal vulnerability:
- Redacting victim faces in some domestic violence cases but not others
- Different treatment based on who requests footage
- Varying standards for high-profile versus routine cases
Prevention: Document clear standards in written policy, use standardized checklists, conduct consistency audits, provide ongoing training.
Mistake 4: Missing Deadlines
State laws mandate specific FOIA timeframes (typically 10-45days). Missing these creates automatic violations, court-ordered expedited releases, settlements ranging from $3,750 upward, and reputational damage.
Prevention: Implement workflow tracking systems, allocate adequate resources based on historical volumes, establish escalation procedures, consider automated solutions for high-volume scenarios.
VIDIZMO Redactor: Purpose-Built for Law Enforcement

Modern agencies require solutions combining automation, compliance, and security. VIDIZMO Redactor provides:
AI-Powered Multi-Modal Redaction:
Unlike competitors offering video-only solutions, VIDIZMO provides unified redaction across video, audio, images, and documents through a single interface. AI automatically detects faces, license plates, PII in transcripts, and text in documents.
Advanced Detection Capabilities:
While basic tools detect faces and plates, VIDIZMO's Vision AI identifies street signs, vehicle types, weapons, signatures, and custom objects specific to law enforcement. Object detection supports equirectangular (360-degree) images, a capability competitors lack.
Compliance-Ready Features:
VIDIZMO meets CJIS, FIPS140-2, and GDPR requirements with built-in audit logging, chain of custody tracking, and secure encryption. The platform supports FOIA exemption coding directly in the redaction workflow.
Deployment Flexibility:
Agencies can deploy VIDIZMO on-premises for complete data control, in secure cloud environments (Azure, AWS), or through hybrid configurations. This flexibility allows meeting agency-specific security policies and compliance requirements.
For agencies ready to strengthen body camera redaction, understanding these legal requirements and technological options provides the foundation for sustainable, compliant programs serving both transparency and privacy.
Ready to strengthen your body camera redaction program?
Learn about AI-powered redaction capabilities designed specifically for law enforcement challenges, or explore FOIA compliance solutions that streamline public records management.
People Also Ask
Agencies must redact faces of minors, victims of sensitive crimes (sexual assault, domestic violence), bystanders not directly involved, medical information and treatment scenes, personally identifiable information(addresses, phone numbers, SSNs) visible or spoken, license plates under DPPA requirements, and confidential informant identities. Requirements vary by state. California AB 748 requires release within 45 days with appropriate redactions, while Illinois exempts most footage unless specific conditions exist (complaints filed, force used, investigations pending). Washington presumes footage is public requiring broader redactions before release.
Manual redaction is extremely time-intensive. Secure Redact industry data shows manually redacting a 10-minute video typically requires 8 hours of specialized work using traditional video editing software. This includes frame-by-frame review to track faces, identify license plates, review audio for spoken PII, and conduct quality control checks. For a 45-minute incident, agencies may need 36+ hours of redaction work. Automated AI-powered tools reduce this time by 85-90%, processing the same 10-minute video in approximately 10-30 minutes with human oversight.
No. Illinois Attorney General guidance explicitly states technological capability is not valid basis for denying requests. The December 2024 Harvey settlement for $3,750 demonstrates claiming lack of technology can result in legal liability. The lawsuit alleged "willful and intentional violations" whether from "individual subjective malfeasance or structural bad faith through underfunding and mismanagement. "Agencies lacking internal capabilities must acquire appropriate tools or outsource to qualified vendors. Resource constraints don't excuse FOIA non-compliance.
Three primary layers govern redaction: (1) Freedom of Information Act and state public records laws requiring disclosure with exemptions for privacy, ongoing investigations, and law enforcement techniques; (2) Driver's Privacy Protection Act prohibiting release of personal information connected to license plates visible in footage;(3) State-specific privacy laws like California AB 748 (45-day release requirement), Illinois Body Camera Act (footage generally exempt unless flagged), and Washington state law (presumption of public access). Additionally, footage containing Protected Health Information may trigger HIPAA considerations, and crime victim protection laws add further requirements.
Inadequate redaction creates serious consequences including FOIA violation lawsuits with settlements ranging from $3,750 upward, DPPA penalties for improperly disclosed license information, civil privacy tort claims from affected individuals, witness relocation costs when addresses exposed, and reputational damage with loss of community trust. Common mistakes include metadata exposure (GPS coordinates in files), reflection captures(faces visible in mirrors, windows, glass), inconsistent redaction standards, and inadequate audio redaction where visual content is blurred but audio contains names, addresses, or medical information. Agencies should implement multi-layer quality control including automated detection, specialist review, supervisory approval, and random audits.
Jump to
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

Ensuring Privacy and Compliance with Video Redaction for Transport
Object Detection–Based Video Redaction Software: Features & Accuracy

No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think