GDPR Video Redaction Requirements and Best Practices
by Zain Noor, Last updated: February 5, 2026, ref:
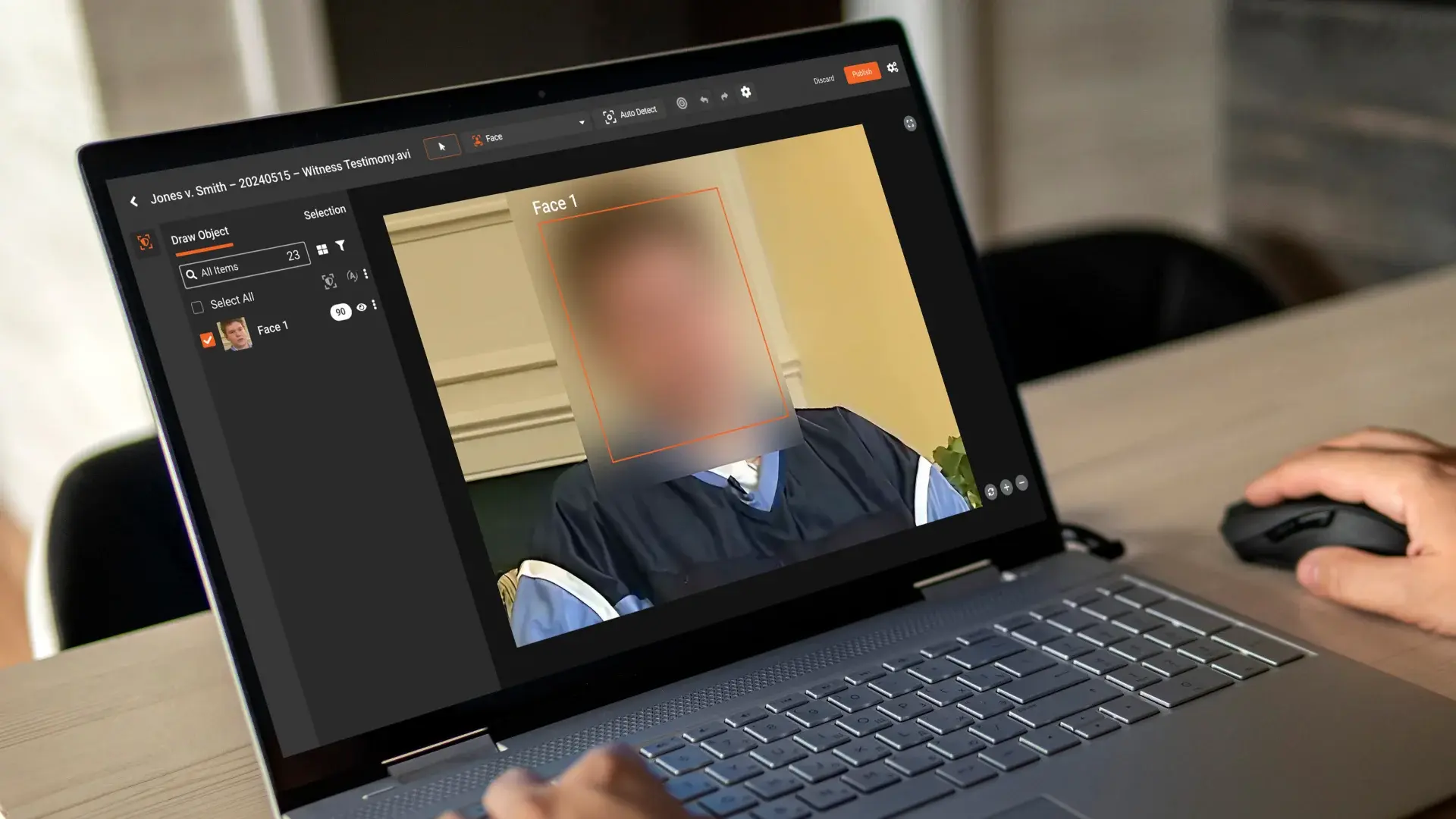
Video now plays a central role in modern operations, and under GDPR, its use comes with strict obligations, whether the footage comes from CCTV systems, body-worn cameras, workplace meetings, interviews, inspections, or customer interactions. But as video volume increases, so does the risk of exposing personal data. According to European regulators, organizations remain fully responsible for safeguarding any identifiable information captured in video, even when the recording was made for legitimate business or security purposes.
This is where GDPR video redaction requirements become essential. Any footage containing identifiable individuals, voices, documents, or contextual clues must be carefully handled before being disclosed. Failure to redact such videos can result in unauthorized disclosures, SAR violations, and costly GDPR noncompliance penalties.
In this blog, we break down GDPR expectations, what qualifies as personal data in video, when redaction becomes mandatory, and how platforms like VIDIZMO Redactor provide an end-to-end, compliant approach to automated visual and audio redaction.
What Is Video Redaction Under GDPR?
Video redaction is the process of obscuring or removing identifiable personal data captured in video or audio. GDPR applies to any media that can identify a natural person, directly or indirectly. This includes both obvious and incidental identifiers.
Examples of personal data requiring redaction include:
- Faces and physical characteristics
- License plates
- Tattoos, clothing, or unique features
- Employee badges
- On-screen documents, dashboards, or digital displays
- Spoken names, phone numbers, addresses, and customer details
Modern redaction tools, such as VIDIZMO Video redaction solution, help detect these identifiers automatically across video, audio, and even documents or images. With AI-powered detection and frame-by-frame accuracy, such platforms significantly reduce manual review time and lower the risk of human error.
Why GDPR Requires Video Redaction
GDPR’s core principles directly influence how videos must be handled:
Data minimization
Only the necessary information should be processed or shared. Redaction removes unrelated individuals before disclosure.
Integrity and confidentiality
Unredacted footage often contains sensitive or private data. Redaction ensures compliance when footage is passed across departments or external parties.
Purpose limitation
Footage captured for security or operational needs cannot expose unrelated individuals when used for training, auditing, or legal requests.
Rights of the data subject
Article 15 grants individuals the right to obtain a copy of their data. When multiple people appear, redaction is required to avoid revealing data belonging to others.
Platforms like VIDIZMO Redactor support these principles by offering automated workflows, audit logs, and secure access controls for compliant processing.
What Counts as Personal Data in Videos?
GDPR defines personal data broadly, and in video that includes visual, audio, and contextual identifiers.
Visual Identifiers
- Faces, bodies, gait, and posture
- Tattoos or unique markings
- Vehicle license plates
- Employee ID cards or uniforms
- Residential or workplace addresses visible in the frame
- Visible screens or documents revealing private information
Audio Identifiers
- Names spoken during calls or interactions
- Customer information or phone numbers
- Addresses or private discussions captured in recordings
Special Category Data
Footage may also contain sensitive information, such as:
- Health details in patient care recordings
- Religious or political symbols
- Biometric identifiers that could be used to uniquely identify a person
With VIDIZMO Redactor, organizations can redact both visual and audio identifiers, including transcripts, based masking for sensitive spoken information, helping maintain compliance even in complex recordings.
Legal Basis for Video Redaction Under GDPR
GDPR does not explicitly use the word "redaction," but it clearly establishes obligations that make redaction a necessary safeguard for any organization's processing of video containing personal data. Multiple GDPR articles directly shape when and how redaction must occur, making it an integral part of compliant data handling.
Article 5, Data Minimization & Confidentiality
Organizations are required to process only the minimum amount of personal data needed for a specific purpose. When sharing or disclosing videos, redaction ensures that only relevant portions remain visible, preventing unnecessary exposure of unrelated individuals. The confidentiality principle also requires organizations to protect personal data from unauthorized access, making redaction essential when footage leaves its original context.
Article 6, Lawful Processing
Every use of personal data must rely on a valid legal basis. Sharing unredacted footage may exceed the scope of the legal basis under which the video was originally captured. Redaction reduces the amount of personal data being further processed, aligning the disclosure with GDPR’s lawfulness requirement.
Article 9, Special Categories of Data
If video footage includes sensitive information, such as health indicators, religious symbols, biometric identifiers, or union membership, organizations must apply heightened protection. Redaction becomes crucial to prevent accidental exposure of special category data, especially when the footage is shared externally or used for non-original purposes.
Article 32, Security of Processing
GDPR mandates appropriate technical and organizational measures to secure personal data. Redaction functions as one such measure, reducing the risk of unauthorized identification or disclosure. For high-risk processing activities, like CCTV monitoring, investigations, or HR recordings, applying irreversible redaction strengthens overall security.
Article 15, Subject Access Requests (SARs)
Individuals have the right to access their personal data. When multiple people appear in a video, organizations must provide the requester data without revealing the identities of others. Redaction is therefore mandatory in nearly all SAR responses involving visual or audio identifiers.
Platforms like VIDIZMO Redactor help organizations meet these legal expectations through secure processing environments, audit trails, automated detection, and controlled redaction workflows, ensuring consistency and compliance throughout the disclosure process.
When Is GDPR Video Redaction Mandatory?
Redaction is required when the video is being:
- shared with external parties
- disclosed publicly or upon request
- processed for SARs
- used for HR or internal investigations
- submitted to courts or regulators
- provided to insurers or legal counsel
- transferred outside the EU
Common Scenarios Where GDPR Makes Redaction Mandatory
Subject Access Requests (SARs/DSARs)
When an individual requests access to a video in which they appear, organizations must respond within one month. Footage often includes other individuals who have not given consent. GDPR prohibits exposing their identities. Redaction ensures the requester receives their personal data while protecting everyone else.
For long-duration CCTV clips, manual redaction becomes nearly impossible, making automation a critical requirement.
Public Disclosures or Freedom of Information (FOI) Requests
Government bodies, municipalities, universities, and public organizations may need to release footage due to transparency laws. Before any footage becomes public, GDPR requires full anonymization of every identifiable person who is not the subject of the disclosure. This includes faces, voices, clothing details, name tags, and even contextual markers.
Workplace HR Recordings and Internal Investigations
Recordings of interviews, misconduct investigations, performance evaluations, training sessions, or staff meetings often capture personal or sensitive data. HR teams must ensure that only individuals relevant to the case remain identifiable. Others, such as employees walking in the background or appearing incidentally, must be redacted to avoid exposing internal information.
Security, CCTV, and Surveillance Footage
CCTV captures high volumes of personal data, often from people who are not aware they were recorded. When sharing surveillance footage with third parties, such as security firms, law enforcement, facility management partners, or external investigators, GDPR requires redacting all bystanders, minors, and unrelated persons to avoid unlawful disclosure.
Cross, BorderTransfers
Sharing video outside the EU/EEA triggers additional GDPR safeguards under international data transfer rules. Redacting identifiable data reduces exposure risks and strengthens compliance when transferring videos to jurisdictions with different privacy standards. Redaction becomes a practical measure to minimize data and align with GDPR’s requirement for “data minimization” during transfers.
How VIDIZMO Redactor Helps Organizations Meet Mandatory Redaction Requirements
Managing these scenarios manually is resource-intensive and prone to error, especially for long recordings, large CCTV archives, or repeated SAR requests. VIDIZMO Video Redaction Software streamlines mandatory redaction by automatically detecting multiple identifiers, including faces, bodies, screens, license plates, and audio elements. The platform generates consistent, irreversible redactions while maintaining audit logs, access controls, and encryption to support GDPR, compliant workflows.
VIDIZMO Redactor enables organizations to fulfill their legal obligations efficiently while protecting the privacy of all individuals appearing in video content.
Key GDPR Video Redaction Requirements
GDPR places strict expectations on how organizations must handle personal data within video recordings. These requirements are not optional for technical preferences; they stem directly from GDPR’s core legal principles, including data minimization, confidentiality, accountability, and the rights of data subjects. As a result, organizations must adopt structured, repeatable, and secure redaction practices to ensure compliance.
Below are the key requirements, expanded with deeper GDPR context:
Accurate Identification of All Personal Data
Under GDPR, personal data includes any visual or audio element that can identify a natural person. This means organizations must detect all instances of personal data within a video, not only clear faces, but also:
- Reflections in windows or mirrors
- People are partially visible in the background
- Identifiers on clothing, workplace badges, or equipment
- Text on documents, screens, or whiteboards
- Voices in crowded or long recordings
Because videos often contain overlapping, fast, moving, or low-quality elements, organizations must ensure thorough review processes or adopt automated detection methods to reduce errors. GDPR expects organizations to apply reasonable measures to identify and protect all personal data captured in the footage.
Permanent, Irreversible Reduction
Redaction must make personal data impossible to reconstruct. GDPR considers anonymization valid only when the reidentification risk is eliminated. Techniques must ensure that even with advanced tools or contextual clues, individuals cannot be identified.
Irreversible redaction is critical in situations such as:
- Responding to Subject Access Requests
- Sharing recordings with external bodies
- Publishing or disclosing footage
Temporary masking, translucent blurring, or overlays that can be reversed do not meet GDPR’s standards for anonymization.
Maintain Proper Audit Trails
GDPR’s accountability principle requires organizations to prove their compliance with decisions. Every redaction action must be documented, including:
- Why was redaction needed
- Who performed it
- What portion of the video was altered
- When the redaction was completed
Audit logs provide transparency during regulatory reviews, internal investigations, or legal disputes.
Protect the Original Footage
Organizations must preserve original recordings in their unaltered form. GDPR requires secure handling of both original and redacted versions, ensuring:
- Originals remain tamper-proof and accessible only to authorized personnel
- Redacted copies are created for disclosure or sharing
- Storage systems use encryption and access controls
Protecting originals ensures evidence integrity and supports compliance with data accuracy and accountability principles.
Meet SAR and Disclosure Timelines
GDPR requires organizations to respond to SARs within one month, even when requests involve large volumes of video data. This means organizations need efficient processes to:
- Locate relevant footage
- Identify the requester’s personal data
- Redact all unrelated individuals
- Produce a clear, accessible output
Manual redaction for long or complex footage can be slow, so workflow planning and resource allocation are essential for meeting deadlines.
Limit Data Disclosure
GDPR mandates that organizations share only what is necessary for the intended purpose. This includes:
- Cropping or segmenting footage to limit exposure
- Removing unrelated individuals or sensitive contextual information
- Redacting background audio or screens containing private data
Minimizing the amount of personal data disclosed ensures compliance with the principles of data minimization and purpose limitation.
Use Secure, Compliant Redaction Tools
Any software used for redaction must incorporate strong security and governance measures. These may include:
- Encryption during processing and storage
- Access controls and user permissions
- Audit logs and version tracking
- Support for on-premises or compliant cloud deployment options
Using secure tools ensures that personal data remains protected throughout the redaction process.
How Automated AI Video Redaction Helps Ensure GDPR Compliance
AI-powered redaction tools solve many compliance challenges by:
- Automatically detecting faces, bodies, screens, text, and license plates
- Masking spoken names and identifiers through the transcript, based on audio redaction
- Generating compliance, ready audit logs
- Maintaining original footage integrity
- Processing large volumes quickly
VIDIZMO Redactor extends this even further by offering redaction across:
- Video
- Audio
- Images
- Documents
This provides a unified solution for all sensitive data formats, making it easier for organizations to comply with GDPR holistically, especially when dealing with mixed media evidence, HR documentation, or large CCTV datasets.
Best Practices for GDPR, Compliant Video Redaction
GDPR‑compliant video redaction is not just a technical task but an operational process that requires structure, consistency, and clear governance. The following best practices help organizations build a reliable, audit‑ready redaction framework that aligns with GDPR’s requirements for data minimization, confidentiality, accuracy, and accountability.
Establish an Internal Redaction Policy
A formal redaction policy ensures consistency across departments and reduces compliance risk. A comprehensive policy should:
- Define which types of video content require mandatory review
- Identify who is authorized to perform redaction
- Outline escalation procedures for complex or sensitive footage
- Provide clear rules for handling SAR‑related recordings
- Specify which identifiers must always be redacted
This policy becomes especially important during audits, investigations, or when multiple teams handle video content.
Use Purpose, Built Redaction Tools
General video editors are not designed to meet GDPR standards. Many overlays they apply can be reversed, and they lack audit logs, secure access controls, and AI detection features. Purpose‑built tools ensure:
- Permanent masking that cannot be undone
- Automatic detection of visual and audio identifiers
- Secure handling of original and redacted files
- Consistent application of GDPR requirements across all videos
Purpose‑built solutions significantly reduce human error and ensure redaction is carried out using compliant, repeatable methods.
Validate Redaction Outputs
Redaction mistakes can result in GDPR violations, so validation is critical. Validation should include:
- Reviewing the full video in real time to ensure no identifiers were missed
- Checking each segment where movement or lighting changes occur
- Reviewing audio transcripts to confirm all sensitive speech has been redacted
- Ensuring text on screens, documents, or labels is fully masked
A second review process is recommended for high‑risk disclosures, such as SAR responses or public releases.
Train HR, Legal, Security, and IT Teams
Redaction requires collaboration across multiple departments. Training should cover:
- GDPR principles and obligations
- How to identify personal and special‑category data
- When redaction is required vs. when footage cannot be lawfully shared
- How to operate the organization’s redaction tools and workflows
Well‑trained teams reduce compliance gaps and ensure requests are handled efficiently and consistently.
Automate When Handling High Volumes
Manual redaction becomes impractical when dealing with:
- Long CCTV recordings
- Body‑worn camera footage
- Multi‑participant meetings or interviews
- High numbers of SARs or regulatory requests
AI automation speeds up detection, reduces labor costs, and helps organizations meet tight GDPR deadlines. While human oversight is still required, automation handles repetitive, time‑consuming tasks and improves overall accuracy.
Implement Secure Storage and Access Controls
Videos often contain sensitive and special‑category data, so secure storage is essential. Access controls must:
- Limit who can view, edit, or export both original and redacted videos
- Log every access or modification
- Encrypt files during storage and transfer
- Maintain strict separation between original footage and redacted copies
Secure video handling ensures that personal data is protected at every stage of processing.
For organizations researching compliant tools, exploring video redaction software such as VIDIZMO Redactor can significantly reduce workload and compliance risk while supporting structured, audit‑ready workflows.
How VIDIZMO Redactor Supports GDPR Video Redaction Compliance
While GDPR does not mandate specific technologies, organizations increasingly adopt automation to meet accountability, accuracy, and timeliness expectations. VIDIZMO Redactorprovides a comprehensive approach to GDPR, compliant redaction across all major media formats, video, audio, images, and documents, ensuring personal data is properly anonymized before disclosure.
VIDIZMO’s AI models automatically detect faces, bodies, license plates, screens, text, and objects within video frames, reducing the risk of overlooked identifiers. For audio, a transcript-based redaction allows organizations to mask names or sensitive details without editing entire segments. The platform also supports document and image redaction, making it easier to handle evidence packs, HR files, and other mixed media records.
Designed for secure processing, VIDIZMO offers encryption, role-based access permissions, detailed audit logs, and the ability to maintain unaltered originals while producing fully redacted output files. These capabilities help organizations meet GDPR obligations, respond faster to SARs, and streamline multidepartment compliance workflows.
For teams evaluating tools, VIDIZMO Redactor serves as a unified video redaction software solution that balances accuracy, scalability, and compliance transparency.
Start Your Free Trial Today - No Credit Card Needed
People Also Ask
What are the GDPR video redaction requirements?
GDPR video redaction requirements involve identifying and removing personal data in video and audio before sharing it. Faces, voices, screens, and other identifiers must be masked to prevent unauthorized disclosure.
Why is video redaction necessary under GDPR?
Video redaction prevents exposing individuals who appear in recordings when footage is shared or used for Subject Access Requests. GDPR requires protecting personal data across all media types.
What personal data in videos must be redacted for GDPR compliance?
Any identifier that reveals a person’s identity, such as faces, license plates, spoken names, or visible documents, must be removed before disclosure.
Is blurring enough to meet GDPR video redaction requirements?
Blurring is acceptable only if the redaction is irreversible. Reversible overlays do not comply with GDPR anonymization expectations.
When must organizations redact video under GDPR?
Redaction is required for SARs, public disclosures, CCTV footage sharing, legal requests, and any situation where unrelated individuals appear in the footage.
Does GDPR require audio recording in videos?
Yes. If spoken dialogue reveals names, contact details, or sensitive information, the audio must be redacted or muted.
How does GDPR affect CCTV footage sharing?
CCTV footage must be redacted to remove non-relevant individuals before sharing it externally, ensuring compliance with GDPR’s principles of data minimization and confidentiality.
Jump to
You May Also Like
These Related Stories
.webp)
Top 7 Video Redaction Software for PII Redaction (Reviewed in 2025)
.webp)
How Insurance Firms Streamline Compliance with AI Redaction Tools



No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think