Redaction Best Practices for Federal Agencies: A Comprehensive Guide
by Rafay Muneer, Last updated: January 13, 2026, ref:

The risks associated with mishandling sensitive information are growing rapidly. If you're part of a federal agency, you're feeling this pressure more than ever. You’re responsible for navigating a labyrinth of regulatory demands while ensuring sensitive information stays confidential.
Think about it: what happens if an email or report containing personal data or classified details slips through the cracks? Not only does this put individuals’ privacy at risk, but it can also leave your agency facing severe legal and financial consequences. The stakes are high, and you’re not alone in feeling the weight of these responsibilities.
Whether you're handling Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) requests, responding to legal discovery, or managing classified government information, there's one thing you're probably worried about: how can you ensure that nothing sensitive is left exposed in your documents?
The answer lies in redaction best practices. But we’re not just talking about manually blacking out text with a marker (if only it were that simple!). We’re diving deep into the precise, tech-powered world of digital redaction—an essential practice that, when done right, safeguards your agency’s reputation and legal standing.
Incomplete Redaction Leads to Costly Mistakes
The reality is that even a minor redaction error can open the floodgates to major problems.
Imagine this: You’re tasked with responding to a FOIA request. Hundreds, if not thousands, of pages of documents must be reviewed, edited, and shared within a tight deadline. Missing even one sensitive item could result in the exposure of personal data, such as Social Security numbers or confidential government details.
Or maybe you're preparing documents for litigation, and one incorrectly redacted section could violate client privilege or expose crucial evidence.
Mistakes like these happen more often than you think. Redaction errors not only compromise privacy but also put agencies at risk for lawsuits, fines, and irreparable damage to their reputation. And the ripple effect? Loss of public trust.
In fact, federal agencies have been criticized for inconsistent redaction practices. Some agencies fail to meet compliance standards, which can lead to public scrutiny or legal penalties.
Does this sound familiar?
For legal professionals, compliance officers, and records managers, the sheer volume of data combined with the ever-increasing complexity of regulations creates a high-risk environment. The task of properly redacting sensitive information isn't just difficult—it’s overwhelming.
If you're struggling with this, you're not alone.
Rules for Redacting Documents in Federal Agencies
Redacting documents within federal agencies is not discretionary—it is governed by strict legal and regulatory rules. Failure to follow these rules can result in unlawful disclosure, compliance violations, and loss of public trust. Below are the core rules agencies must follow when redacting documents for public release, litigation, or records requests.
1. Redact Information Required by Law, Not Preference
Redaction must be based on legal authority, not internal discretion. Agencies are only permitted to redact information explicitly protected under federal laws and regulations.
Key laws governing redaction include:
- Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) – Requires disclosure while protecting exempt information under FOIA Exemptions (b)(1) through (b)(9)
- Privacy Act of 1974 – Protects personally identifiable information (PII)
- HIPAA – Requires redaction of protected health information (PHI)
- Federal Rules of Civil Procedure (FRCP) – Governs redaction in legal discovery
- Classified Information Procedures Act (CIPA) – Protects national security information
Only information covered by these authorities may be redacted.
2. Apply FOIA Exemptions Correctly and Consistently
Under FOIA, agencies must release records unless the information falls under a specific exemption. Common FOIA redaction rules include:
- Exemption (b)(1): Classified national defense or foreign policy information
- Exemption (b)(3): Information prohibited from disclosure by statute
- Exemption (b)(6): Personal privacy (e.g., Social Security numbers, home addresses)
- Exemption (b)(7): Law enforcement records that could cause harm if disclosed
Each redaction must be defensible, clearly tied to the appropriate FOIA exemption, and applied consistently across all documents.
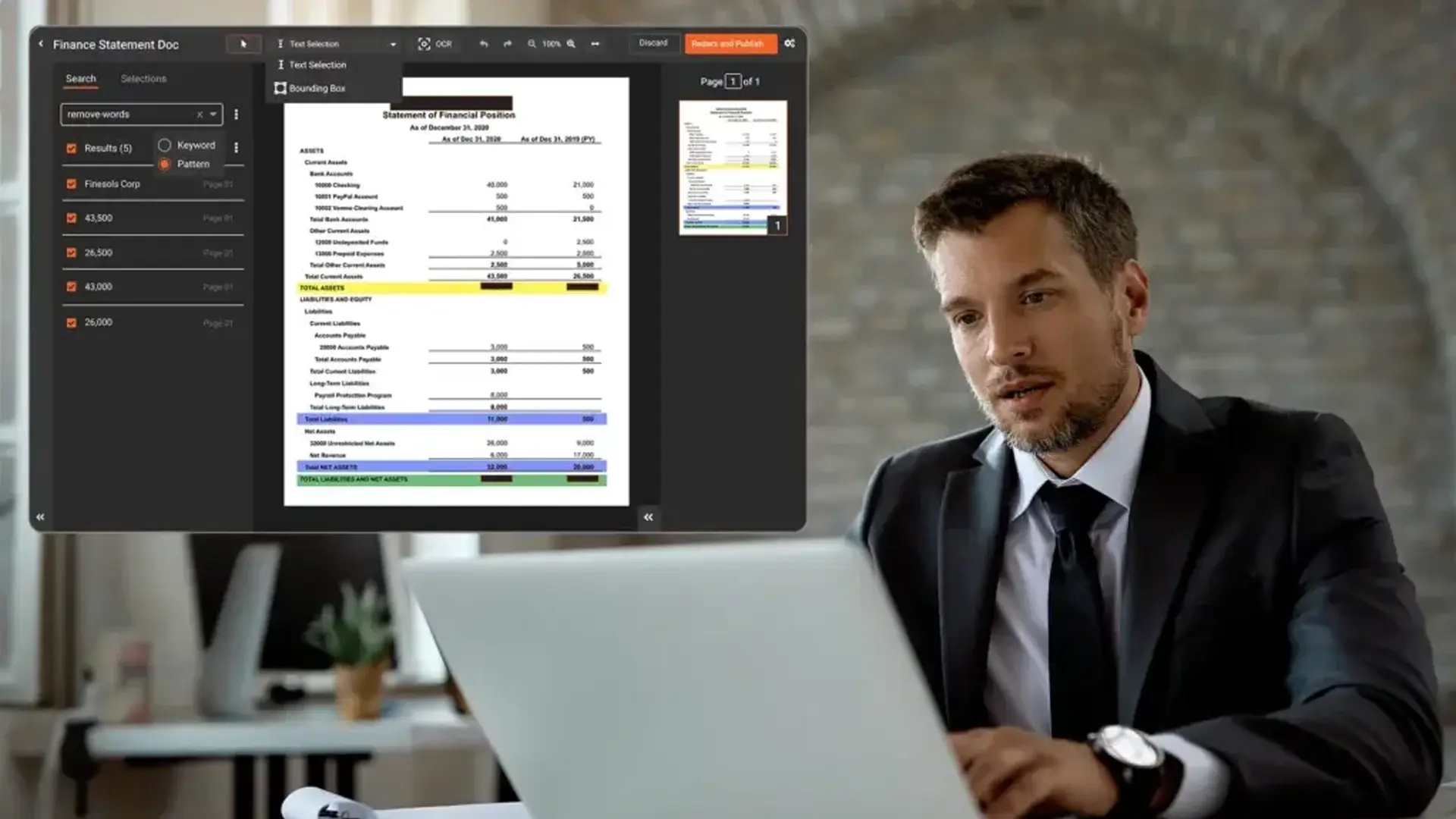
3. Permanently Remove Sensitive Data, Visual Hiding Is Not Enough
A critical rule of redaction is that sensitive data must be permanently removed, not merely hidden.
Agencies must ensure that:
- Redacted text cannot be revealed by copying, searching, or adjusting layers
- Metadata, comments, tracked changes, and hidden text are removed
- OCR text behind images is also redacted
Simply covering text with black boxes or shapes does not meet federal redaction standards.
4. Redact All Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
Federal agencies are required to redact PII wherever disclosure could result in a privacy violation or security risk.
Examples of PII that must be redacted include:
- Social Security numbers
- Dates of birth
- Driver’s license or passport numbers
- Home addresses and personal phone numbers
- Financial account details
Even partial exposure of PII can constitute a compliance failure.
5. Maintain Redaction Accuracy Across All File Formats
Redaction rules apply to all document types, not just PDFs or text files.
Agencies must ensure redaction accuracy in:
- Emails and email attachments
- Scanned documents and images
- Audio and video files
- Case files and digital evidence
Tools used for redaction must support OCR, multimedia redaction, and bulk processing to ensure no sensitive data is missed due to file format limitations.
6. Use Audit Trails and Quality Assurance Checks
Every redaction action must be traceable and verifiable.
Federal redaction rules require:
- Audit logs showing who redacted what and when
- Secondary review or quality assurance checks before release
- Documentation supporting why the information was redacted
These measures protect agencies during audits, legal challenges, and public scrutiny.
7. Do Not Over-Redact or Under-Redact
Over-redaction violates transparency obligations, while under-redaction exposes sensitive information. Agencies must strike a legally defensible balance.
Best practice rules include:
- Redacting only the minimum necessary information
- Releasing non-exempt portions of documents whenever possible
- Ensuring redactions do not obscure meaningful context unnecessarily
Balanced redaction preserves both public access and legal compliance.
8. Regularly Review and Update Redaction Rules
Redaction requirements evolve as laws, court rulings, and technology change.
Agencies must:
- Review redaction policies annually
- Update procedures based on new legal precedents
- Train staff on changes to redaction rules and tools
Staying current reduces the risk of outdated practices leading to compliance violations.
The Risks of Inadequate Redaction Practices
It’s easy to underestimate the damage a single redaction mistake can cause. But for federal agencies, the stakes are incredibly high.
Legal Ramifications
One improperly redacted document can expose your agency to lawsuits or legal challenges. Whether it’s sensitive information about a citizen’s personal data or confidential government operations, the legal consequences of inadequate redaction can be crippling.
Public Relations Nightmares
When sensitive information is accidentally released to the public, it’s not just an internal issue—it becomes a very public problem. Trust is everything for federal agencies, and a breach can permanently damage the relationship with the citizens you serve. Once that trust is lost, it's hard to regain.
Fines and Sanctions
Regulatory bodies are becoming increasingly strict about data breaches, especially when federal agencies are involved. Agencies can face hefty fines for non-compliance with redaction standards, especially under privacy regulations like HIPAA and the Privacy Act. These financial penalties add up quickly, impacting already stretched budgets.
Operational Inefficiency
Relying on outdated or manual redaction processes doesn’t just increase risk; it slows everything down. With FOIA request deadlines looming and the volume of requests increasing each year, inefficient workflows can lead to bottlenecks, frustrated staff, and delays that put your agency at further risk of non-compliance.
So, how do you get it right?
Best Practices to Achieve Flawless Redaction
If you’re serious about protecting your agency and the data you manage, you need to get your redaction process right. Here’s how.
Invest in the Right Redaction Software
Let’s be honest—manual redaction isn’t feasible. For federal agencies dealing with vast quantities of sensitive information, automation is key.
The right redaction software should allow you to:
- Automatically detect and redact sensitive information based on pre-configured criteria (e.g., Social Security numbers, addresses, classified data).
- Generate audit trails that allow you to review and track every redaction action performed.
- Support compliance with federal laws and regulations, such as HIPAA, FOIA, and the Privacy Act.
- Redact across multiple formats (e.g., PDFs, emails, images) to cover every type of document in your agency’s database.
By implementing redaction software with these features, your agency can dramatically reduce the risk of errors while speeding up the document review process. Automation ensures consistency and accuracy in handling large volumes of sensitive information.
Establish Clear Redaction Policies and Procedures
Without standardized policies, redaction becomes inconsistent. Every team member might redact documents differently, creating confusion and increasing the risk of missing sensitive data.
To combat this, clear, agency-wide redaction policies should be implemented. These should include:
- Specific redaction criteria (e.g., personally identifiable information, classified government information) based on legal guidelines.
- Protocols for document review and approval before any redacted material is released to the public.
- Comprehensive training programs to ensure that all employees understand the redaction process and the tools they need to use.
Having these policies in place ensures uniformity in redaction across your agency, reducing the chances of mistakes and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Provide Ongoing Training and Updates
Redaction isn’t a one-time task, and neither is learning how to do it correctly. As new regulations emerge and technology advances, employees must stay updated to ensure compliance and avoid errors.
- Conduct regular training sessions to refresh employees’ understanding of redaction tools and protocols.
- Provide scenario-based learning where teams work through real-life examples of sensitive data redaction to reinforce best practices.
- Update training materials as needed when regulations, agency policies, or redaction software change.
Ongoing training ensures that employees stay informed on the latest redaction techniques, reducing the risk of outdated methods causing errors.
Implement Layered Security Measures
Redaction is only one piece of the puzzle in protecting sensitive information. Layered security measures can enhance your redaction processes and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information before, during, and after redaction.
- Role-based access controls (RBAC) ensure that only authorized personnel can access, edit, or review documents that require redaction.
- Encrypt documents containing sensitive information, ensuring that even if a breach occurs, the data remains secure.
- Audit access logs to track who has accessed or modified sensitive documents, allowing you to monitor compliance and detect suspicious activity.
Combining these security measures with effective redaction practices minimizes the risk of data exposure and enhances overall data protection.
Conduct Regular Redaction Audits
Even with automation, mistakes can happen. Regular audits help catch potential issues in redacted documents and refine your redaction process.
- Establish a formal audit process to periodically review redacted documents and ensure that sensitive information has been properly removed.
- Use automated quality assurance tools that check documents for errors, such as hidden metadata or missed sensitive data, which could lead to unintentional disclosures.
- Gather feedback from staff and auditors to identify areas of improvement in your redaction processes and tools.
Conducting audits not only helps catch mistakes before they become public but also allows your agency to continuously improve its redaction practices.
Stay Compliant with Evolving Regulations
Laws like FOIA, HIPAA, the Privacy Act, and even GDPR for international dealings are continuously evolving. Staying up to date with these regulations is crucial to ensuring your redaction process remains legally compliant.
- Regularly review legal requirements that affect how your agency handles and redacts sensitive information.
- Work closely with legal teams to ensure that redaction policies align with the latest compliance standards.
- Review precedent cases where improper redaction led to legal issues, using these examples to improve internal practices.
By staying on top of evolving regulations, your agency can avoid the financial penalties and reputational damage that come with non-compliance.
Ensure Redaction Across All Formats
Sensitive information is often stored in many formats—emails, PDFs, images, video, and even audio. Effective redaction must extend beyond text-based documents.
- Use redaction tools that support a wide variety of file formats, ensuring that sensitive information is consistently removed across all media types.
- Leverage Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to extract text from images and videos for thorough redaction.
- Test redaction processes across different file formats to ensure that sensitive data is fully removed and not just visually hidden.
Supporting multiple formats ensures that no sensitive information is left vulnerable in overlooked file types.
Establish a FOIA Response Workflow
FOIA requests are a common challenge for federal agencies, often requiring the redaction of vast amounts of sensitive information. A well-structured FOIA response workflow can improve the accuracy and speed of handling these requests.
- Designate a dedicated FOIA team responsible for handling requests, redacting documents, and ensuring compliance with federal regulations.
- Use redaction software that integrates with FOIA management systems, streamlining the process of identifying and removing sensitive data.
- Create a timeline and checklist for handling FOIA requests, ensuring that documents are reviewed, redacted, and released on time.
Establishing a streamlined workflow ensures that FOIA requests are handled efficiently, reducing the risk of errors and missed deadlines.
Focus on Usability in Redaction Tools
A key factor in successful redaction implementation is ensuring that the tools your agency uses are user-friendly and accessible to everyone involved in the redaction process.
- Choose intuitive redaction software that allows users to easily select areas to redact and verify results without extensive training.
- Ensure that the software integrates seamlessly with existing systems, like document management platforms, to minimize disruptions.
- Offer support resources such as user manuals, video tutorials, and helpdesk support to assist employees in quickly resolving any technical challenges they face.
By focusing on usability, you empower your team to redact sensitive data efficiently and accurately, reducing both training time and the risk of human error.
Redact Metadata and Hidden Information
It’s not just what you see on the surface of a document that needs redaction—metadata, revision histories, and hidden text can also contain sensitive information.
- Ensure that your redaction process includes metadata removal, which can often reveal file creation dates, authors, or even previous versions of a document.
- Check for hidden data layers such as comments, tracked changes, and watermarks, which can easily be overlooked during manual redaction.
- Use tools designed to scrub documents clean of any potentially harmful metadata before releasing them to the public.
Key Takeaways
-
Redaction Is Critical for Protecting Sensitive Information: Mishandling classified data can lead to significant legal, financial, and reputational damage. Redaction is necessary to ensure sensitive information is protected in compliance with federal regulations.
-
Manual Redaction Is Inefficient and Error-Prone: Traditional methods, such as manual blacking out of documents, are outdated and prone to mistakes. Automated redaction tools are essential for handling large volumes of sensitive information with greater accuracy and speed.
-
Compliance with Regulations Is a Must: Federal agencies must adhere to strict laws like FOIA, HIPAA, and the Privacy Act when redacting documents. Failure to comply can result in costly penalties, legal action, and loss of public trust.
-
Implement Clear Redaction Policies and Procedures: Standardized redaction practices across your agency are necessary to ensure consistency and reduce the likelihood of human error. Comprehensive policies and ongoing training are essential.
-
Automated Redaction Software Boosts Efficiency: Investing in software that automatically detects and redacts sensitive information ensures more reliable, faster, and compliant document processing, especially when dealing with large data volumes.
-
Ensure Layered Security Measures: Redaction should be combined with strong security measures, such as role-based access controls and encryption, to protect documents from unauthorized access or exposure during the redaction process.
-
Regular Audits and Continuous Improvement: Conducting regular audits of redacted documents and updating redaction policies ensures that your agency stays compliant with evolving standards and reduces the risk of accidental disclosures.
People Also Ask
What is the difference between redaction and data masking?
Redaction permanently removes sensitive information from a document, making it ideal for public releases, while data masking hides information temporarily, allowing access to authorized users. Redaction is irreversible, whereas data masking retains original data for specific users.
What are the rules for redacting documents?
The rules for redacting documents require that sensitive information be permanently removed based on legal authority, not discretion. Federal agencies must redact information protected under laws such as FOIA, the Privacy Act, HIPAA, and applicable court rules. Redactions must be irreversible, consistently applied, supported by audit trails, and limited to information that qualifies for protection, ensuring compliance while maintaining transparency.
What are the most common mistakes agencies make during redaction?
Common mistakes include manually redacting documents, inconsistent redaction standards across teams, and failing to test or audit redacted documents before they are released to ensure all sensitive information is properly obscured.
Can AI redaction tools handle all sensitive information?
AI-powered redaction tools are effective at identifying and redacting common sensitive information like PII or PHI, but it’s important for agencies to manually review documents to ensure that no context-specific information is overlooked.
How often should agencies update their redaction policies?
Agencies should review and update their redaction policies at least annually or whenever there are significant changes in regulations, compliance standards, or internal workflows to ensure continued compliance with data protection laws.
What types of documents require redaction in federal agencies?
Documents such as FOIA requests, legal discovery documents, classified reports, and any documents containing Personally Identifiable Information (PII) or sensitive government data require redaction to protect privacy and ensure compliance with federal regulations.
What is the best software for automating redaction in federal agencies?
The best software for automating redaction is one that allows for bulk processing of documents, identifies sensitive information automatically, supports multiple file formats (like PDFs and emails), and provides an audit trail for compliance.
Why is manual redaction not enough in federal agencies?
Manual redaction is not enough because it’s time-consuming, prone to human error, and inconsistent. It can lead to sensitive information being overlooked or improperly redacted, resulting in legal and reputational risks.
How can agencies prevent human error during redaction?
Agencies can prevent human error by implementing automated redaction software, establishing clear redaction procedures, providing regular training, and conducting audits to ensure accuracy and consistency in the redaction process.
What are the legal consequences of improper redaction in federal agencies?
Improper redaction can lead to legal penalties, including fines, lawsuits, and the potential loss of public trust. Agencies may also face compliance issues under laws such as HIPAA, FOIA, and the Privacy Act if sensitive information is improperly disclosed.
Jump to
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

Document Redaction for Government: Balancing Transparency and Privacy
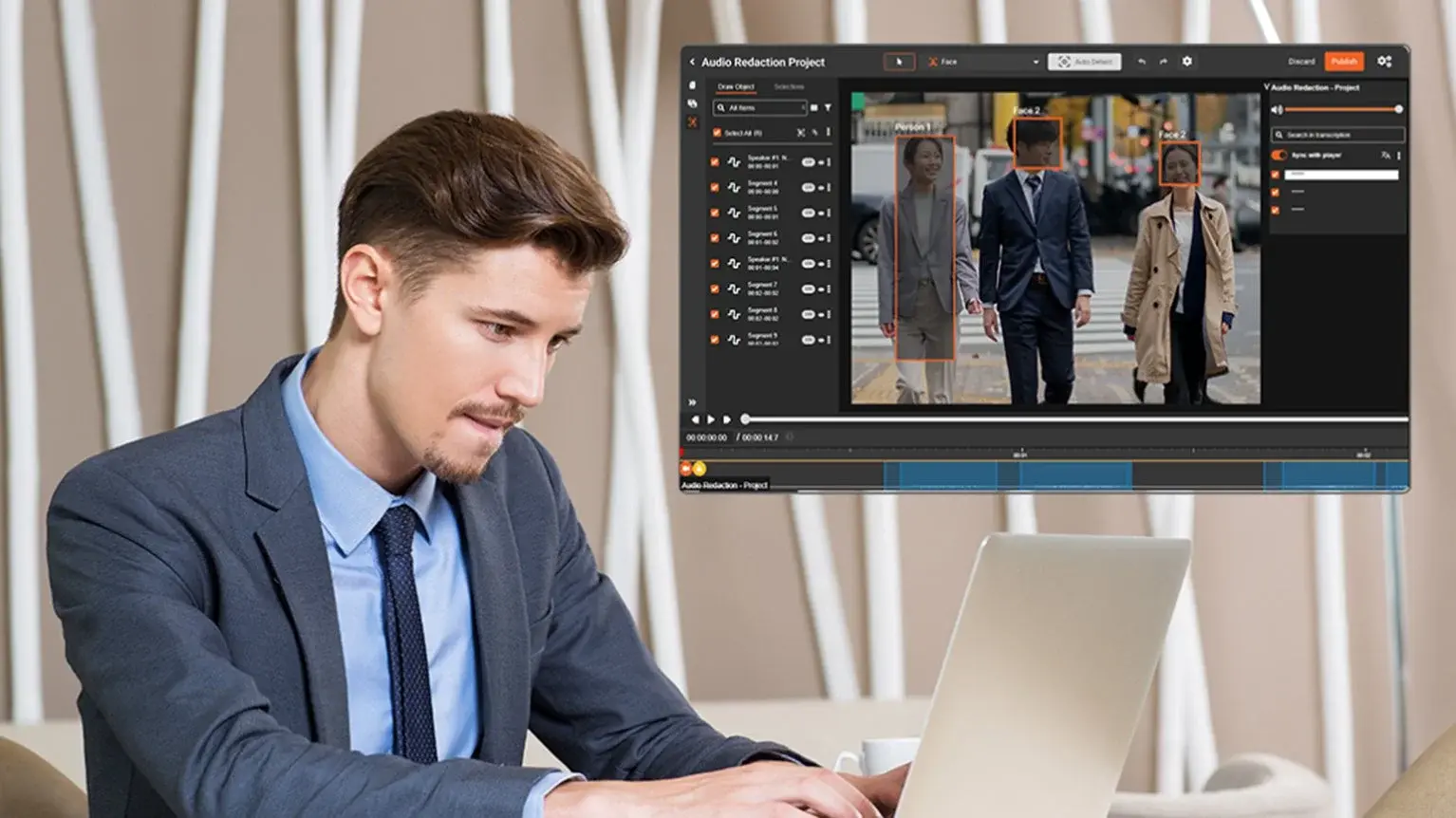
Audio Redaction Software for HIPAA and GDPR Compliance

No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think