Data Redaction vs Data Masking for Law Enforcement
by Hassaan Mazhar, Last updated: December 25, 2025, ref:
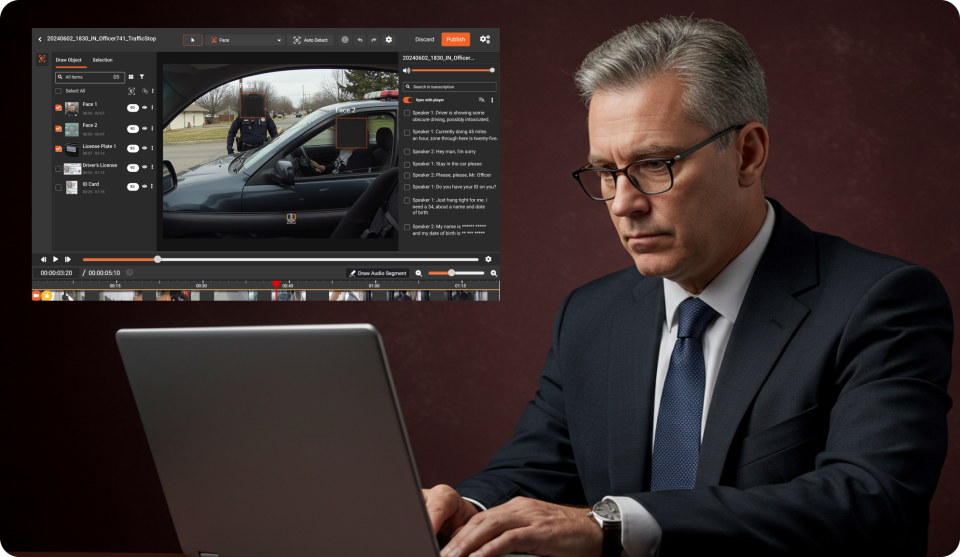
As law enforcement agencies manage growing volumes of digital evidence, two terms are often used interchangeably, but shouldn’t be:
Data Redaction and Data Masking.
While both aim to protect sensitive information, they serve very different purposes, especially when evidence must be disclosed publicly, shared with prosecutors, or defended in court.
Understanding the distinction is critical, not just for compliance, but for operational accuracy, legal defensibility, and public trust.
Why This Distinction Matters in Law Enforcement
Law enforcement data is unique. It includes:
- Body-worn camera footage
- CCTV and surveillance video
- Interview and dispatch audio
- Incident reports and case files
- Personally identifiable information (PII) of victims, juveniles, and witnesses
These materials are often subject to:
- FOIA and public records requests
- Discovery obligations
- Court review and evidentiary standards
Choosing the wrong protection method can lead to:
- Accidental disclosure of sensitive information
- Evidence being challenged in court
- Compliance violations
- Loss of public confidence
That’s why agencies must clearly distinguish when to redact and when to mask.
What Is Data Redaction?
Data redaction is the permanent removal or obscuring of sensitive information from a file before it is shared or released.
In law enforcement, redaction is commonly used to protect:
- Faces of bystanders or juveniles in video
- Names, addresses, or phone numbers in documents
- Audio segments containing PII
- License plates or identifying objects
Once redacted, the sensitive information cannot be recovered from the released version.
Common Redaction Methods
- Blurring or pixelating faces in video
- Muting or bleeping audio segments
- Blacking out text in documents
- Removing metadata fields
Redaction is essential when evidence is:
- Released to the public
- Shared outside the agency
- Presented in court
What Is Data Masking?
Data masking, by contrast, is the obfuscation or substitution of sensitive data, typically while retaining the original underlying information.
Instead of removing data, masking replaces it with:
- Placeholder characters (e.g., XXX-XX-1234)
- Randomized values
- Tokenized references
Masking is commonly used in:
- Databases
- Analytics systems
- Testing or training environments
Masked data is usually:
- Reversible (with access)
- Not intended for public release
- Used internally for operational or analytical purposes
Why Data Masking Is Usually the Wrong Choice for Evidence Release
While data masking has value in IT and analytics, it introduces serious risks when applied to law enforcement evidence:
- Masked data may still be technically retrievable
- It can create confusion about what was altered
- Courts and prosecutors often expect clear redaction, not substitution
- Public disclosures require irreversible protection
In short, masking protects systems, while redaction protects people.
How Automated Redaction Software Fits In
Modern law enforcement agencies increasingly rely on automated redaction software to handle the scale and complexity of today’s evidence.
Advanced redaction platforms can:
- Detect faces, license plates, and spoken PII automatically
- Allow human review and manual correction
- Produce audit trails for every redaction action
- Ensure consistent application of policies across cases
Solutions like VIDIZMO REDACTOR are designed specifically for law enforcement redaction workflows, supporting video, audio, image, and document redaction while maintaining full accountability.
Importantly, redaction software focuses on irreversible protection, not data masking—making it suitable for FOIA responses, discovery, and court submissions.
When Masking Still Has a Role in Law Enforcement
Although masking is not appropriate for public evidence release, it can still be useful for:
- Internal data analysis
- Training simulations
- System testing environments
The key is using each method in the correct context, rather than treating them as interchangeable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Agency
When deciding between redaction and masking, law enforcement agencies should ask:
- Will this data be released outside the agency?
- Could this evidence be reviewed in court?
- Is irreversible protection required?
- Do we need auditability and chain of custody?
If the answer to any of these is “yes,” redaction, not masking, is the appropriate choice.
Final Takeaway
Data redaction and data masking may sound similar, but for law enforcement, the difference is profound.
- Redaction protects people, cases, and agencies during disclosure.
- Masking protects systems and internal workflows.
Understanding and applying the right approach is essential to maintaining compliance, credibility, and public trust.
Want to See Law Enforcement Redaction in Action?
If your agency is evaluating how to handle sensitive data safely and at scale:
Jump to
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

Legal Redaction Software: Ensuring Data Privacy & Compliance

How To Implement Redaction Without Losing Data Accuracy



No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think