What Does Redacted Mean in Law: A Practical Guide for Legal Teams
by Hassaan Mazhar, Last updated: January 8, 2026, ref:

Your team spends weeks preparing a production set, only to pull it back at the last minute because someone spots an unblurred face in bodycam footage or an unmasked social security number in a PDF. Work stops, stress spikes, deadlines slide, and no one is fully sure what “properly redacted” even means across all the evidence types you handle.
This is the hidden tax you pay when your organization is not aligned on what does redacted mean in law. You are not just blacking out content. You are deciding what the court, regulators, counterparties, and the public are allowed to see, and what must be shielded for privacy, privilege, or statutory reasons.
Once you scale beyond a few documents, that ambiguity turns into real risk. Miss a single identifier in a video or transcript, and you face data breaches, sanctions, or damaged credibility with the bench and regulators.
This guide explains what does redacted mean in law in clear, operational terms. It defines the legal redaction meaning, connects it to business risk, and shows how it applies not only to traditional documents but also to video and audio evidence that now dominates discovery and regulatory response.
Defining what does redacted mean in law for legal practitioners
At its core, the answer to what does redacted mean in law is straightforward. Redaction is the deliberate removal or masking of specific information from a legal record before disclosure, while preserving the rest of the content for use as evidence or for public access.
In other words, legal redaction meaning focuses on targeted omission, not wholesale withholding. You produce the record, but in a controlled form that complies with law and protects sensitive interests.
Key aspects of the redacted documents legal definition in practice include:
- Identifying content that is legally protected or restricted from disclosure
- Obscuring only that content, not the entire record
- Maintaining the evidentiary integrity and usability of the remaining material
- Leaving an audit trail that explains what was redacted and under which authority
So when courts, regulators, or counterparties ask what is redaction in law, the operative idea is balance. You must balance transparency and disclosure obligations against privacy, confidentiality, and statutory limits.
Legal redaction meaning across documents, video, and audio
Traditionally, when people discuss what does redacted mean in law, they picture black bars over text. That is still common, but it is only part of the landscape. The legal redaction meaning now spans multiple evidence formats, each with its own risks.
Legal document redaction in text records
Redacting legal documents in text formats typically involves:
- PDFs and scanned records
- Word processing files converted to production formats
- Spreadsheets and tabular data exports
In these cases, the redacted documents legal definition covers removal of:
- Personal identifiers (names, SSNs, addresses, phone numbers, emails)
- Protected health information under HIPAA or similar regimes
- Payment card data and account numbers
- Trade secrets and competitively sensitive information
- Attorney client privileged material and attorney work product
Redaction in court records for video evidence
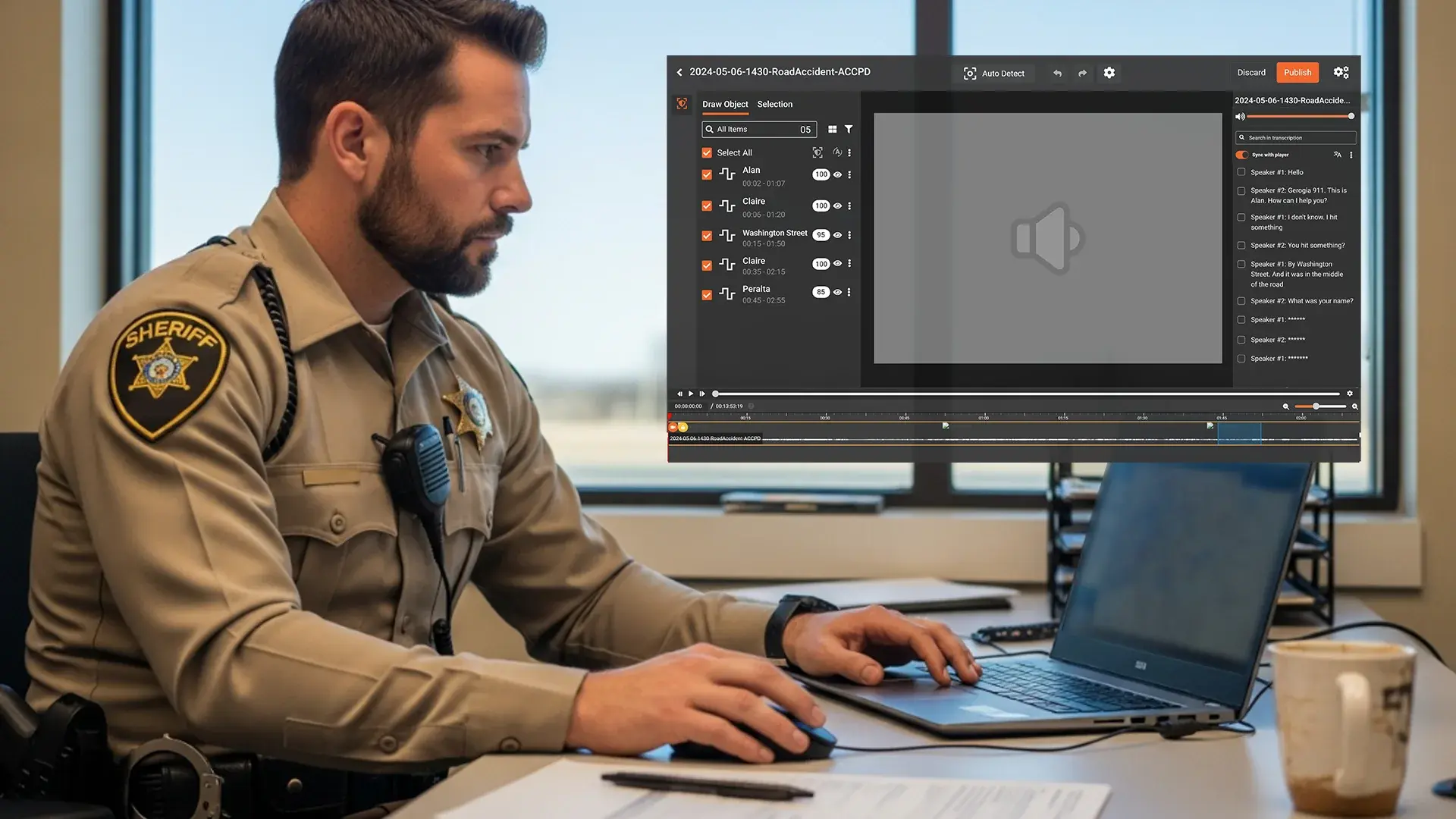
Redaction in court records increasingly involves video. Body worn camera footage, security feeds, and mobile recordings all reach the record. In that context, what does redacted mean in law extends to:
- Blurring faces, license plates, and other visual identifiers
- Masking screens, documents, or whiteboards visible in frame
- Obscuring locations or landmarks that reveal home or work addresses
The legal redaction meaning here is visual rather than textual, but the same principles apply. You must only conceal what is necessary, maintain chain of custody, and ensure that redaction artifacts do not mislead the fact finder.
Redaction in audio and transcripts
Audio recordings and their transcripts create another layer. To redact legal documents that contain transcripts and to handle pure audio files, you may need to:
- Mute names, phone numbers, or sensitive phrases in the audio
- Replace redacted sections with beeps or silence while preserving timestamps
- Black out or bracket corresponding portions in the transcript
Here again, what is redaction in law is not just deletion. It is controlled concealment while preserving context so that the record remains intelligible and usable.
Why redaction is required in law: privacy, privilege, and compliance
To fully understand what does redacted mean in law, you need to connect it to the legal bases that require it. Across jurisdictions, three drivers recur.
Privacy and data protection obligations
Modern privacy laws expect organizations to limit disclosure of personal data. Legal redaction meaning often flows directly from:
- General data protection regulations in relevant jurisdictions
- Sectoral privacy rules in finance, healthcare, and telecom
- Children and minors protection statutes
When you disclose records in litigation or respond to public records requests, privacy rules usually require you to redact identifiers that are not strictly necessary for the stated purpose. That covers both traditional legal document redaction and masking identities in video and audio.
Attorney client privilege and work product
Privilege is another central element in what is redaction in law. You frequently must produce communications or reports while preserving privileged portions. That can involve:
- Redacting legal advice embedded in mixed business communications
- Masking references to litigation strategy in investigative reports
- Obscuring counsel names or email addresses in large scale email reviews
Courts expect you to be precise. Over redaction can trigger in camera reviews and judicial skepticism. Under redaction can lead to subject matter waiver of privilege. This is where a clear, shared understanding of what does redacted mean in law becomes operationally critical.
Regulatory and statutory compliance
Many regulations do not merely suggest redaction. They demand it. Legal document redaction may be required by:
- Bank secrecy and anti money laundering statutes
- Industry specific supervisory rules
- Open records laws that specify exempt categories
When you file redacted documents with agencies or produce records for exams, your redaction in court records and regulatory records must map cleanly to these enumerated exemptions. Otherwise, you risk penalties or forced re production under tight deadlines.
Business pain: operational risks of inconsistent legal document redaction
From a distance, what does redacted mean in law may sound like a technical detail. Up close, inconsistent understanding translates into real business pain. Legal, compliance, and records leaders often face:
- Manual, fragmented workflows. Different teams redact legal documents, video, and audio in different tools, with no standard rules or templates.
- High error rates. Human review alone struggles to catch every identifier, especially in long videos and multi hour recordings.
- Re work and delays. Late stage discovery or regulator feedback forces you to redo entire productions, burning hours and budget.
- Audit gaps. You cannot easily show who redacted what, when, and under which legal basis.
- Reputational risk. One high profile redaction failure in court records or public releases can damage trust with stakeholders.
When the organization has no common answer to what does redacted mean in law across media types, every matter becomes a bespoke project. That is not sustainable at scale, especially with rising volumes of multimedia evidence.
Redaction in court records and litigation workflows
In litigation, the redacted documents legal definition comes under direct scrutiny. Courts expect redaction to be precise, justified, and documented. Problems often surface in three areas.
Protective orders and confidentiality designations
Protective orders often describe what does redacted mean in law for a given matter. They specify categories of confidential information and procedures for filing redacted documents. Risk arises when:
- These definitions are not translated into concrete redaction rules for reviewers
- Teams handling video and audio evidence are not aligned with document review teams
- There is no mechanism to validate that the same standards apply across all evidence
Public access to court filings
Many jurisdictions presume public access to filings. To protect privacy and trade secrets, parties must redact legal documents and multimedia exhibits before they appear in public dockets. In practice, that involves:
- Applying court specific redaction rules for personal data identifiers
- Ensuring that video and audio exhibits mask nonparties and minors
- Producing a clear record of what has been redacted and why
When courts review disputes about redaction in court records, they often look at process. They want to see a consistent framework, not ad hoc edits made under time pressure.
Learn more about the redaction workflows in law enforcement.
Discovery, productions, and meet and confers
During discovery, what does redacted mean in law is negotiated and refined across parties. Stipulations often cover:
- How to treat sensitive personal data in large data sets
- Standards for redacting or anonymizing video and audio
- Metadata handling, including whether to redact or pseudonymize fields
Without documented, repeatable redaction workflows, you cannot reliably implement these agreements. That leads to disputes, motion practice, and higher outside counsel spend.
How to redact legal documents, video, and audio at scale
To operationalize what does redacted mean in law, organizations move from case by case improvisation to defined, scalable processes. That involves four practical steps.
1. Create a unified redaction policy
First, codify your organizational answer to what is redaction in law. A usable policy should:
- Define protected categories of information across jurisdictions and matters
- Differentiate between mandatory and discretionary redaction
- Cover documents, video, audio, and transcripts in a single framework
- Specify approval flows for sensitive or borderline decisions
2. Standardize media specific redaction rules
Next, translate the policy into format specific playbooks. For example, for legal document redaction in text, define:
- Which personal data fields must always be redacted
- When to use partial redaction, such as masking only parts of IDs
- How to treat headers, footers, and embedded objects
For video and audio, specify:
- Which visual elements must be blurred in each record type
- When to mute, bleep, or silence audio segments
- How to sync changes with transcripts and subtitles
3. Implement technology that understands multimedia
Manual review alone cannot keep pace with current evidence volumes. To align with the real world legal redaction meaning, modern teams use tools that can:
- Automatically detect faces, license plates, and on screen text in video
- Find and mask personal data in documents based on patterns and dictionaries
- Search and redact entities in transcripts, then propagate changes to audio and video
- Log all redaction actions for audit and quality control
The goal is not to automate legal judgment. It is to automate repetitive detection tasks so your experts can focus on edge cases and defensibility.
4. Build review, QA, and audit layers
Finally, treat redaction as a governed process. That means:
- Reviewing samples regularly to verify that standards are applied correctly
- Running validation checks before productions or public releases
- Maintaining logs that tie each redaction decision to policy grounds
These controls turn your definition of what does redacted mean in law into something you can demonstrate to courts and regulators.
People also read: How to Redact Legal Documents Using AI-Powered Redaction Software
Using tools like VIDIZMO REDACTOR for consistent legal redaction
Once your organization knows what does redacted mean in law and has a policy, the next challenge is applying that definition consistently across content types. This is where specialized platforms enter the picture.
As an example, solutions such as VIDIZMO REDACTOR allow organizations to operationalize legal redaction meaning across video, audio, and documents in one place. In practice, teams use this kind of platform to:
- Ingest large volumes of multimedia and text records from different systems
- Apply automated detection of faces, license plates, and on screen text in video
- Redact legal documents and transcripts based on entity detection and pattern matching
- Manually refine or override redaction suggestions where legal judgment is needed
- Produce redacted outputs suitable for court records, regulators, or public portals
The value is less about a single feature and more about alignment. The same core definition of what is redaction in law and the same policy rules can be enforced across formats, matters, and teams.
Governance, auditability, and defensibility of redacted documents
Courts and regulators rarely ask whether your team can draw black boxes. They ask whether you had a sound process. To meet that standard, your approach to what does redacted mean in law should be backed by governance and auditability.
Traceable redaction decisions
Every time someone redacts legal documents or edits a video, the system should capture:
- Who performed the action
- What was redacted and in which record
- When the change occurred
- Why it was made, such as the applicable rule or exemption
This level of traceability allows you to defend your understanding of the redacted documents legal definition in motion practice or regulatory reviews.
Reproducible outputs and policy alignment
Defensibility also depends on reproducibility. If you are asked to explain why a field was redacted in one record but not another, you should be able to point to consistent rules. That requires:
- Centralized policy management for what is redaction in law within your organization
- Shared templates and rulesets for common case types and jurisdictions
- Outputs that embed metadata about redaction operations
When you handle redaction in court records or respond to supervisory inquiries, being able to show that your decisions map to an established framework carries weight.
Conclusion: turning a legal definition into an operational capability
In theory, what does redacted mean in law is a simple concept. In practice, it touches privacy, privilege, compliance, reputation, and day to day workloads for legal and compliance teams.
Organizations that treat legal redaction meaning as a one time training topic struggle as volumes and media types grow. Those that define it clearly, encode it in policy, and implement consistent workflows across documents, video, and audio can reduce risk while protecting their teams from constant rework.
Redaction will only become more central as courts and regulators receive more multimedia evidence and as privacy expectations rise. A clear, operational answer to what is redaction in law is now a core part of legal operations, not a side task delegated at the last minute.
People Also Ask:
What does redacted mean in law in simple terms?
In legal contexts, redacted means that specific information in a record has been deliberately hidden or removed before disclosure, while the rest of the record remains visible and usable. The goal is to comply with legal obligations and protect sensitive data without withholding entire documents, videos, or audio files.
What types of information are typically redacted in legal documents?
Common targets for legal document redaction include personal identifiers, financial account numbers, health information, trade secrets, and attorney client privileged content. The exact scope depends on applicable laws, court rules, and protective orders that define the redacted documents legal definition in a given matter.
How is redaction in court records different from internal redaction?
Redaction in court records must follow specific court rules on privacy and public access, and is subject to direct judicial review. Internal redaction, such as for internal investigations or early case assessments, may be guided more by organizational policy and risk tolerance, although the underlying legal redaction meaning is similar.
What is redaction in law for video and audio evidence?
For video, redaction in law usually involves blurring faces, license plates, screens, or locations that should not be exposed. For audio, it often involves muting or replacing sensitive names, numbers, or phrases while keeping timestamps aligned. In both cases, the purpose is to apply the same privacy and privilege protections that apply to documents, adapted to multimedia.
Is blacking out text in a PDF enough for proper legal redaction?
Simply drawing black boxes over text in a PDF is not always sufficient, especially if the underlying text can still be copied, searched, or recovered. Proper legal document redaction requires removing or irreversibly masking the content at the file level so that it cannot be reconstructed by recipients.
Who is responsible for deciding what to redact in legal matters?
Responsibility for defining what does redacted mean in law for a specific matter usually sits with counsel, often in consultation with privacy, compliance, and records teams. Reviewers and vendors implement those decisions, but legal teams must set the criteria, approve edge cases, and stand behind the defensibility of the approach.
How can organizations ensure consistency in redaction across cases?
Consistency requires a central redaction policy, standardized rules for different media types, and technology that applies those rules uniformly across documents, video, and audio. Governance mechanisms, such as audits and quality reviews, help ensure that your practical application matches your stated definition of what is redaction in law.
Why is automation important for legal redaction at scale?
Automation helps detect faces, identifiers, and entities across large volumes of content that manual reviewers would struggle to process in time. It does not replace legal judgment, but it enables teams to apply their understanding of what does redacted mean in law reliably and efficiently, especially for high volume, multimedia heavy matters.
Can redaction be reversed or challenged?
If redaction is done correctly, the obscured content should not be technically recoverable from the produced record. However, opposing parties or requesters can challenge whether particular information should have been redacted under the law. That is why clear policies, logs, and rationale for each category of redaction are critical for defensibility.
Jump to
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

How Businesses Can Redact Legal Documents and Stay Compliant in 2025

Legal Redaction Software: Ensuring Data Privacy & Compliance


No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think